STEP 1
Note: Temperature and humidity readings can be skewed by the operating temperature of the Tessel. Distancing the the climate module from the Tessel via wires is recommended for accurate readings.
Make a directory inside your “tessel-code” folder called “climate”, change directory into that folder, and initialize a tessel project:
mkdir climate; cd climate; t2 initSTEP 2
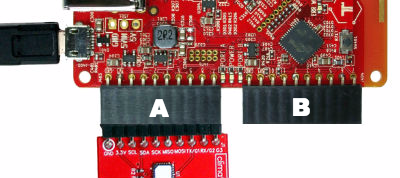
Plug the climate module into Tessel port A with the hexagon/icon side down and the electrical components on the top, then plug Tessel into your computer via USB.
STEP 3
Install by typing npm install climate-si7020 into the command line.
STEP 4
Rename “index.js” to “climate.js” and replace the file’s contents with the following:
// Any copyright is dedicated to the Public Domain.
// http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/
/*********************************************
This basic climate example logs a stream
of temperature and humidity to the console.
*********************************************/
var tessel = require('tessel');
var climatelib = require('climate-si7020');
var climate = climatelib.use(tessel.port['A']);
climate.on('ready', function () {
console.log('Connected to climate module');
// Loop forever
setImmediate(function loop () {
climate.readTemperature('f', function (err, temp) {
climate.readHumidity(function (err, humid) {
console.log('Degrees:', temp.toFixed(4) + 'F', 'Humidity:', humid.toFixed(4) + '%RH');
setTimeout(loop, 300);
});
});
});
});
climate.on('error', function(err) {
console.log('error connecting module', err);
});Save the file.
STEP 5
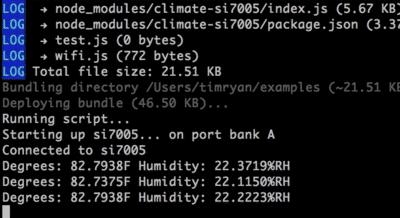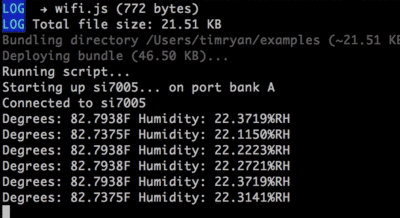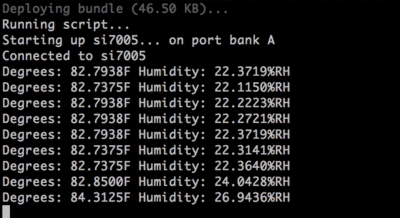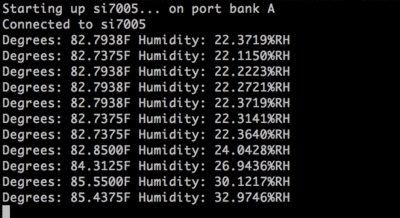
In your command line, t2 run climate.js See the temperature and humidity change if you cup your hands and breathe on the module.
Bonus: Change the code so the temperature reads out in celsius rather than Fahrenheit.
STEP 6
What else can you do with a climate module? Try a community-created project.

