How many times have VPs asked their design teams: “Can’t one designer just handle it all?”
On paper, the overlap between UI and UX design looks tempting. In practice, merging UX and UI too early is how you end up with a gorgeous front end nobody understands. Think of a long-haul flight: the UX designer plans the route, trims turbulence, and checks the weather. The UI designer pours the coffee, dims the lights, and makes the cabin feel like home. Same plane, same destination, wildly different responsibilities.
Stakeholders care because every extra click and every unlabeled button can be leak in the revenue pipe. Keep the leaks small and your retention chart flattens in the right place. Let them grow and you’re leaving money on the table. Simple as that.
What a UX designer really does
A strong UX design lead is half detective, half architect. The detective side conducts user research, digs for motives and pain points; the architect side draws a blueprint the entire squad can build on.
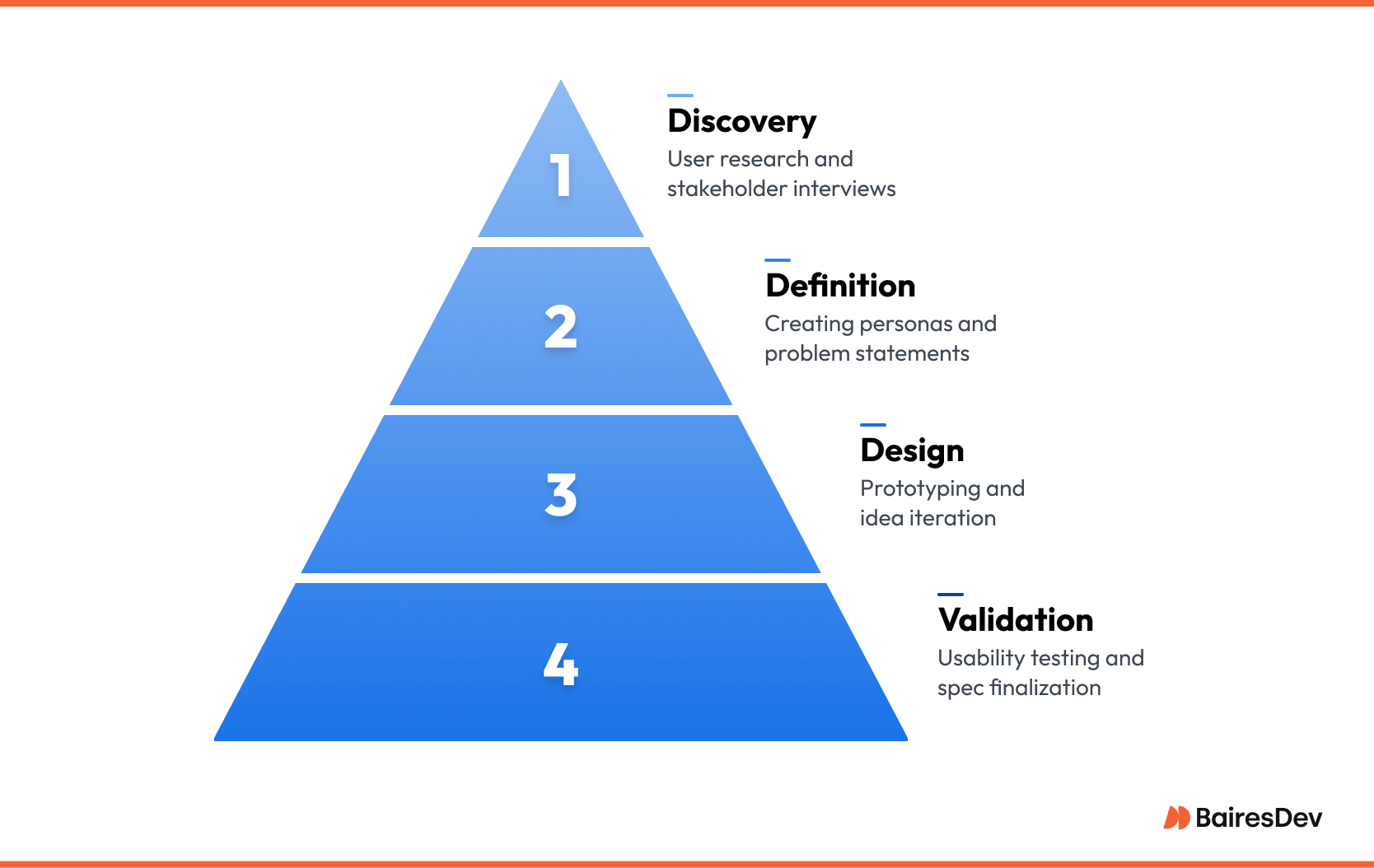
Discovery
Before a single wireframe appears, UX specialists run stakeholder interviews, scrape analytics, and watch user flows in real time. The focus is on the end user, not vanity metrics.
Definition
Patterns emerge. UX specialists collapse them into one-page personas, user journeys, and a crisp problem statement. If the dev team can’t recite that problem at stand-up, the UX teams rewrites it.
Design
White-board sketches turn into low-fidelity user flows, then clickable prototypes. At this stage, nothing is precious. Teams steal, swap, and throw away ideas at speed because code is still cheap.
Validation
Five usability sessions usually surface eighty percent of the issues. When a concept survives real users, teams refine interactions, document edge cases, and lock the spec so engineers can sprint without second-guessing.
That loop continues until metrics move.
Skills that separate seniors from rookies
Great UX pros share three habits. First, they treat user quotes like clues, grouping them until a pattern becomes obvious. Second, they understand constraints, such as security standards, legacy APIs, the CFO’s budget, and design around them instead of complaining. Third, they can walk into an exec review with one slide and defend a decision in two sentences. No jargon, no TED-Talk pacing, just clarity.
Tools that keep the engine running
UX designers tend to keep their stack lightweight because the process is heavy enough:
- Figma for low-friction wireframes and shared libraries.
- Axure when a flow needs conditional logic or embedded data.
- Maze for overnight remote tests that beat waiting a week for a lab.
- Miro boards so product, design, and engineering may brainstorm asynchronously yet leave a trail.
The software matters less than a culture where sketches hit user eyes within days, not months. That timing saves budget and temper—ask any project manager.
How UX design moves the numbers executives track
A positive user experience does not live in Sketch files; it lives in engagement curves and renewal invoices. A refined flow trims seconds from a task, raises confidence, and cuts support tickets before they flood Zendesk. When the experience feels obvious, churn slides down and lifetime value inches up. In other words, UX is the lever your spreadsheets need, not an aesthetic add-on.
Designers achieve this by mapping each step of the user journey, thinning it its essentials, then validating the new path with real data. The result is a user friendly product architecture so intuitive that users forget they are learning anything at all. Clarity replaces hesitation, and hesitant clicks are where revenue usually leaks.
Industry snapshots
The principles stay the same, but their impact shows up differently in various domains:
- Technology and SaaS
If a B2B platform can trim onboarding from eight screens to five, chances are it will manage to increase activation. - E-commerce
Cart abandonment is really design debt in disguise. Retailers are replacing five-field checkouts with single tap payments to improve conversion and eliminate support queries caused by payment errors. - Healthcare
In healthcare platforms, good UX design helps patients and providers navigate complex systems with clarity. The interface must accommodate different levels of digital literacy and high-stakes decision-making, helping lower user error, improve patient compliance, and ease the burden on support teams. - Finance and Fintech
UX design influences whether users complete key tasks like applying for loans, transferring funds, or setting savings goals. Financial products often involve trust-sensitive interactions, and poor design can introduce confusion or hesitation.
These examples prove the same storyline: thoughtful UX reduces friction, and improving the way the user interacts with the product converts directly to revenue or cost savings.
Collaboration makes the results stick
UX cannot operate as a side gig. UX designers sit with engineers, data analysts, compliance officers, and product owners, translating constraints into informed trade-offs. When everyone shares a single problem statement and a living prototype, planning becomes a negotiation of outcomes, not guesswork.
That alignment is why a strong UX culture is more important than any single hire.
The takeaway for senior technology leaders is clear. Invest in UX research and validation up front, watch adoption curves rise, and let the design debt repayment fund itself through the efficiencies it unlocks.
A quick recap before we hand the baton to UI: the UX designer uncovers what matters, frames the problem, proves the flow, and protects the backlog from “surprise” redesigns. Skip this step, and you’re polishing marble floors over a cracked foundation.
The UI designer: turning blueprints into brand moments
If UX design is the flight path, user interface design is the runway lighting. It tells a customer they are in the right place, guides every step with subtle cues, and leaves a lasting impression once the wheels touch down.
A seasoned UI designer thinks in pixels yet speaks the language of brand equity, load times, and accessibility compliance. Their canvas is every screen, dropdown, and micro interaction that meets a real-world finger or mouse.
Daily work that keeps user interfaces on brand and on target
Before the first component library is pushed to Git, UI designers maps out a visual language that can scale from a six-inch phone to a fifty-inch dashboard. The tasks below happen in short cycles that mirror engineering sprints.
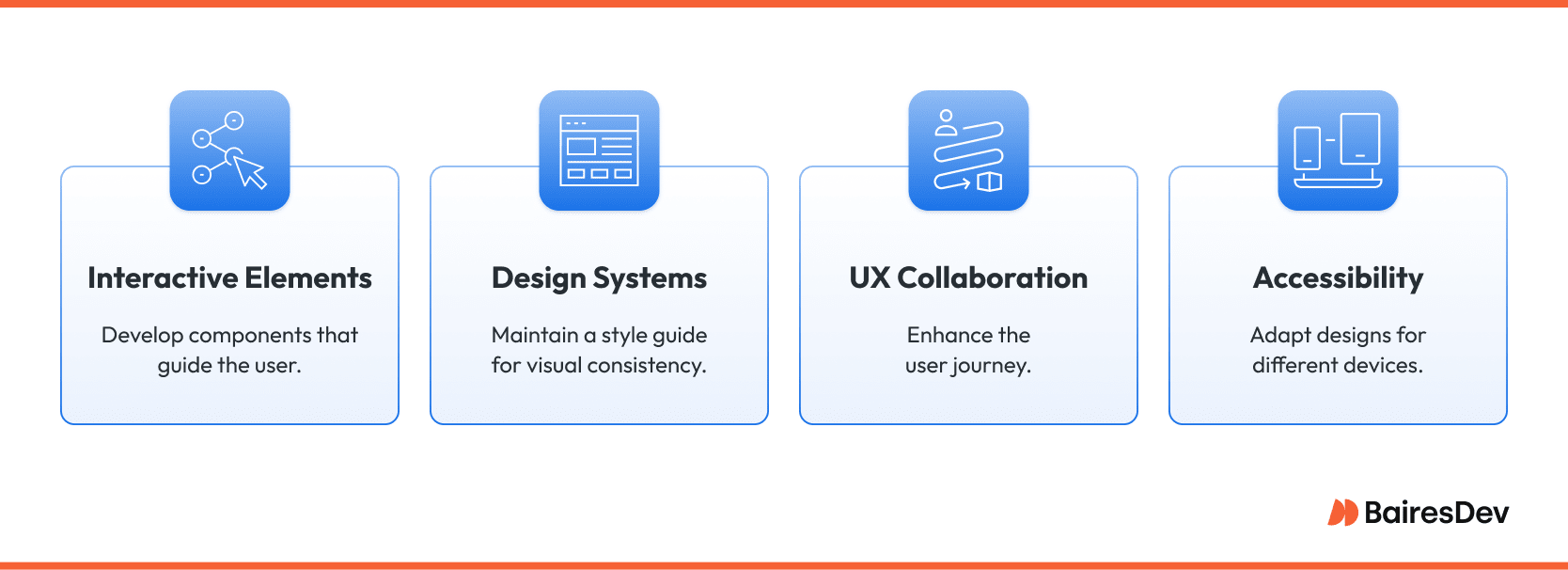
- Designing interactive elements
Buttons, sliders, menus, empty states, and other visual elements are sketched, prototyped, and refined until they guide users without a second thought. - Building and governing a design system
Colors, typography, spacing, and motion rules are captured in a living style guide. Product teams pull from this source of truth to avoid drift and stick to established visual design principles. - Partnering with UX and engineering
Flows proven by research move from grayscale wireframes to vivid high-fidelity comps. The designer pairs with developers to translate every hover state and animation into production code. - Driving accessibility and responsive behavior
Contrast ratios, focus indicators, and breakpoints are audited so the same design feels native on a tablet in sunlight and a laptop in a dim office.
Together these steps in the UI design process remove hesitation from the user journey. The result is a product that feels intentional rather than improvised.
Skills that elevate a UI specialist from decorator to strategist
Great visuals and pixel-perfect design are a given in 2025. What separates top-tier talent is a set of business-aligned habits.
- Visual hierarchy mastery
Each screen tells users what to read first and what can wait. The hierarchy is invisible yet powerful. - Micro interaction craftsmanship
Subtle motion reinforces feedback and reduces cognitive load. A tiny accordion animation can prevent an entire help article. - Atomic thinking
Designers break pages into reusable atoms and molecules which lowers maintenance costs and accelerates releases. - Fluent cross-functional communication
They translate hex codes and leading into metrics the CFO cares about such as reduced support calls or higher checkout completion.
These skills keep aesthetics from becoming superficial decoration. They turn visual polish into measurable impact.
UI design tool belt and when to reach for each item
A UI designer chooses tools that match the problem, not personal habit.
- Figma or Sketch for rapid component iteration and version control with product peers.
- Adobe Illustrator or Affinity Designer for complex vector illustrations and icon sets.
- After Effects or Principle for testing motion patterns before engineering invests.
- Zeplin or Frontify to hand off redline specs and tokens that plug directly into the code base.
The software stack only matters insofar as it sharpens collaboration and accelerates shipping.
Where UI delivers outsized value
While every product deserves a good UI, there are some examples of industries and applications where a good UI can make an outsized impact. Conversely, a poor user interface can wreck retention and revenue.
- SaaS dashboards
Good UI design helps users interpret information quickly. Clear visual hierarchies, updated component libraries, and responsive layouts reduce cognitive overload and allow users to complete tasks more efficiently. - E-commerce product pages
Online retailers rely on visually engaging product pages to influence purchasing decisions. UI designers contribute by optimizing layout, image presentation, and interactive elements such as quick views or comparison features. These visual decisions support higher engagement and help streamline decision-making for the end user. - Streaming media grids
Color coded badges and refined typography help users spot fresh releases instantly, pushing daily watch time up despite an unchanged catalog size. - Telehealth video rooms
Larger call controls and clearer status indicators calm patient anxiety. Attention to color contrast, legibility, and touch-target sizing contributes to a smoother experience, especially for users under stress or with limited tech fluency. - Mobile banking apps
Financial apps require clarity and trust. UI design supports this by surfacing the most-used actions within easy reach, ensuring consistency across screen sizes, and applying design systems that maintain familiarity. The result is reduced error, faster task completion, and a more reliable feel across the product.
Across these sectors the pattern repeats. UI clarity reduces cognitive friction, friction reduction drives the metric that matters most in that industry, and leadership sees a direct link between pixel decisions and quarterly targets.
UX finds the route, UI paves it in the company’s colors. Skip either role and you pay later in rework, brand dilution, or lost users. Invest in both and you create a product team that writes fewer apologies and more release notes.
UX and UI: the strategic split every product owner should respect
UX and UI feel like siblings. Same family, different talents. One brother drafts the blueprint, the other paints the walls and chooses the lighting. Both are essential to move-in day yet they solve different problems on the Gantt chart.
The core remit of each role
A short primer for any VP sorting headcount requests.
UX designers
The job is to discover what users need, translate those needs into flows, and prove the flows remove friction. Research, journey maps, interactive prototypes, and usability studies are the tools of the trade. Success is measured in task completion, lower support tickets, and shorter onboarding.
UI designers
The job is to make those proven flows unmistakably on brand and instantly readable. They create interfaces, color systems, select typography, and create micro-interactions. Success is measured in trust, visual consistency, and reduced cognitive load across devices.
Both designers stare at the same Figma file; they simply handle different layers.
How collaboration turns ideas into revenue
Sequence matters. UX brings evidence to the table first, UI adds emotion second. When that order flips you usually ship pixels that look sharp but solve the wrong pain. On healthy teams the hand-off feels more like a relay exchange than a throw over the wall. Shared component libraries, paired design reviews, and joint demos keep velocity high and rework low.
Tool stacks that pair well together
UX methods lean on research and iteration. Card sorting, A–B testing, click-through prototypes in Maze or UserTesting, workshop boards in FigJam.
UI methods lean on precision and governance. Tokenised design systems in Figma, redline hand-off through Zeplin, motion studies in Principle or After Effects. A single source of truth binds both worlds and prevents the dreaded “looks different in prod” email.
Hiring guide for tight budgets and tight deadlines
Start with the problem you must solve in the next two quarters.
If funnels leak because users are confused, lead with UX. A senior researcher who can run mixed-method studies and refactor flows will save more engineering hours than any color refresh.
If brand perception is stale, or your mobile app looks dated on new hardware, lead with UI. A specialist in atomic design and accessibility compliance will polish surfaces without wrecking performance budgets.
Small teams sometimes chase a hybrid. A true generalist can work for early experiments but expect trade-offs in depth. Complex platforms with regulatory pressure eventually need specialists; the cost of mis-steps is simply too high.
When you screen portfolios look for impact over aesthetics. Ask the candidate to explain a metric that moved because of their design and how they partnered with engineers to get it live.
Key takeaways for senior leaders
UX prevents teams from building the wrong thing.
UI design focuses on the right thing to earn attention and trust.
Treat them as separate levers in your roadmap. Fund both, sequence their work correctly, and your product will feel obvious to new users and credible to existing ones. Skip either lever and the hidden cost will surface later in churn, rework, or lost deals. Your customers may not know the terms UX or UI but they recognise when a product just works. Plan accordingly.
FAQs
What is the difference between UX and UI design?
UX design services create an interactive user experience focused on usability and flow. UI design is about designing interfaces: the visual elements, colors, typography and interactive components that shape the end user’s interaction with the product.
Can one person do both UX and UI design?
Yes, but depends on the project complexity. Smaller teams or startups often look for hybrid designers who can cover both roles. Larger projects usually benefit from dedicated UX and UI experts. This way you get high quality work in each area.
Which is more important, UX or UI design?
Both are important in different ways. UX design meets user needs through functionality and ease of use. UI makes the interface visually appealing and engaging. A good product combines good UI and UX design for a cohesive user experience.
Do UX designers need to know how to code?
Basic knowledge of HTML, CSS and JavaScript can help them work with developers and understand technical constraints during the design process. Bonus points for basic graphic design and web design skills.
Which industries need UX and UI designers?
The tech industry, along with e-commerce, healthcare, finance, entertainment, and many more. Almost every modern digital product or service needs UI and UX specialists.







