Cloud computing has reshaped business since the 2000s. Today, businesses expect the cloud to deliver more than raw storage and compute. The cloud is now judged by how smoothly it scales, how much it saves, and how reliably it runs.
Racks of servers are giving way to rented capacity, and in the process, the cloud has quietly become a pillar of the tech industry. As adoption grows, so does the need for expertise in architecture, security, and automation.
Let’s look at what the future of cloud computing may bring.
What Is Cloud Computing?
At its simplest, cloud computing means getting computing power and storage through the internet instead of a local server room.
When workloads shift from traditional servers to cloud environments, companies gain scalability and efficiency. That shift lets engineering teams spend less time patching servers and more time building new products or services.
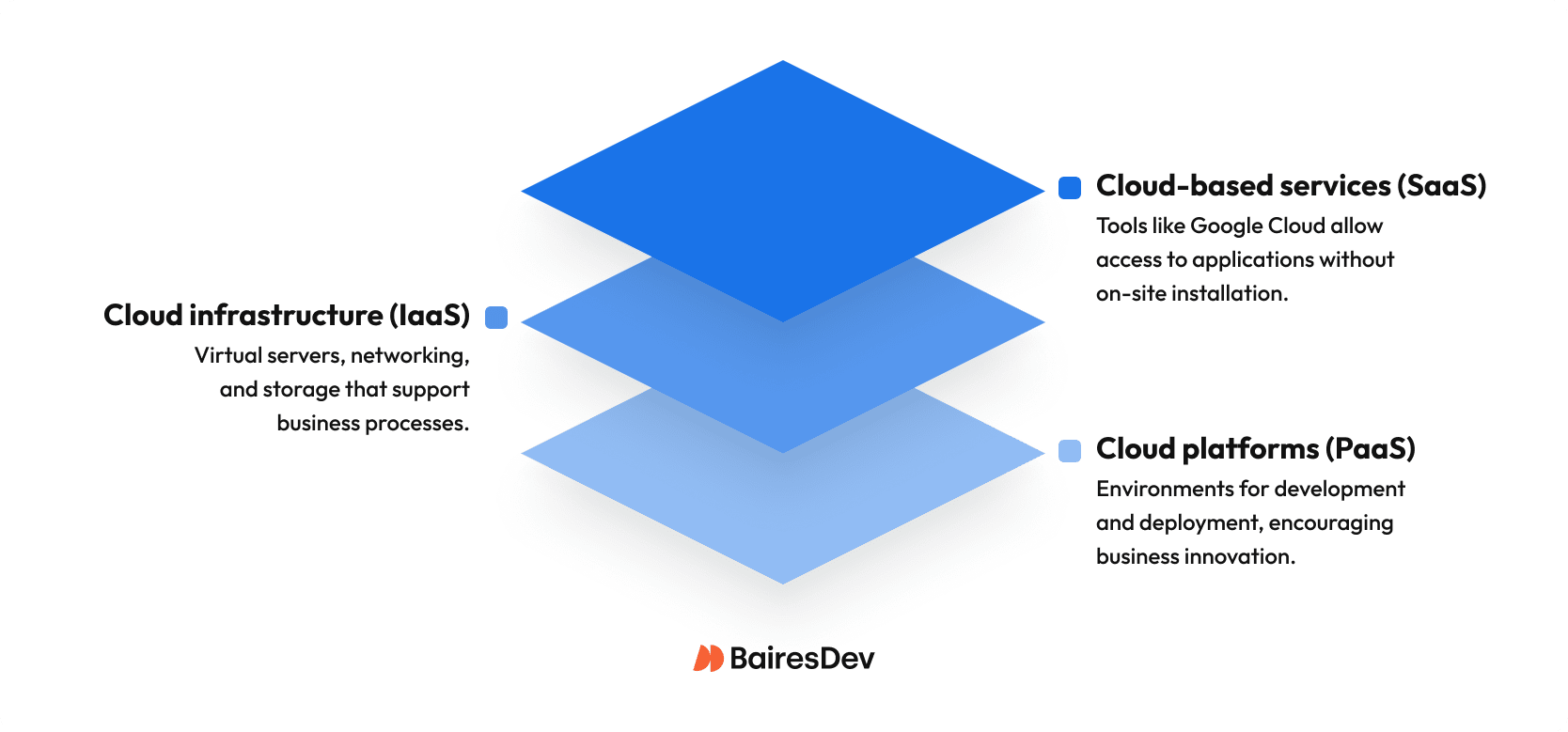
What Is the Future of Cloud Computing – Trends and Technologies
So, where is cloud computing going? Watch for the following emerging and future trends in the coming years.
- Cloud services. Companies increasingly rely on cloud services like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS to run core systems, analytics, and AI/ML workloads without building everything in-house.
- Increased storage capacity. With data volumes exploding, companies increasingly rely on cloud storage not just to archive files but to run the analytics that guide pricing, hiring, and strategy. The future of cloud storage includes offerings to support this growth.
- Internet of Things (IoT). Every factory sensor, smartwatch, and connected fridge generates streams of data that need a digital home — the cloud is that hub.
- Multi-cloud and hybrid environments. Companies are transitioning from using just one cloud service to using many for various purposes. For example, a business might use one provider for IaaS and another to host productivity tools.
Cloud Computing Models
These technologies are helping businesses automate, scale, and secure their operations. Choosing the right mix depends on your goals, data needs, and long-term strategy.
| Technology | Description | Business Benefit |
| Distributed Cloud | Data stored and processed across multiple locations and servers. | Keeps services online even if one server or site goes down. |
| Edge Computing | Data processed near its source (e.g., IoT devices). | Cuts lag time and lets systems act automatically on incoming data. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combines public and private clouds via a shared interface. | Helps firms separate sensitive records from everyday files while staying compliant |
| Serverless Computing | Developers build apps without managing servers. | Faster development and cost efficiency. |
Securing the Cloud
Cloud infrastructure provides scalable resources that support modern IT environments. Providers like Google Cloud and AWS offer built-in security tools—encryption, access controls, and threat detection, among them.
But cloud security doesn’t stop there. Providers protect the infrastructure, while businesses must secure their own data and systems. That means regular audits, strong access policies, and clear data protection rules for your business.
As more companies adopt multi-cloud and hybrid setups, managing risk becomes more complex. Orchestration tools and solid data management practices are key to keeping systems secure and compliant.
New Technologies That Will Transform Cloud Computing Technology Services
Modern cloud platforms help businesses cut costs and improve efficiency. Data centers consume around 176 terawatt-hours annually in the U.S., with projections reaching 12% of total electricity use by 2028. Distributed infrastructure and automation tools support business continuity and reduce downtime.
Real-time analytics offer insights into customer behavior and market trends. Cloud-native development, using microservices and containers, boosts agility and speeds up innovation. AI and machine learning are driving smarter decisions, with 60% of enterprises expected to use them by 2025, and the AI software market projected to hit $125 billion.
Quantum computing is beginning to reshape cybersecurity and financial modeling. Early use cases in finance could generate $622 billion in value, offering new ways to manage risk and optimize performance.
Multi-Cloud and Public Cloud Strategies
Multi-cloud strategies use multiple cloud providers to diversify capabilities and avoid vendor lock-in. Public cloud services, by contrast, offer cost efficiency and scalability, supporting rapid adoption. Businesses that combine these strategies can store data, optimize processes, and ensure resilience.
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud approaches give organizations flexibility to balance workloads across different cloud providers, ensuring they always have access to the best cloud capabilities for specific needs.
For example, one provider may excel in AI-driven cloud services, while another leads in compliance-ready infrastructure. Integrating them effectively requires advanced cloud orchestration, unified data management, and teams skilled in multi-cloud environments.
Prepare for the Future and Don’t Give In to FOMO
Companies may be tempted to take a “fear of missing out” approach in which they rush to move certain processes to the cloud just because others — perhaps competitors—are doing so, instead of first thinking through the “why.”
Automation tools can simplify infrastructure management, but cloud computing services are only useful if they support clear company goals.
Manage multi-cloud deployments smartly
Another aspect of cloud computing that’s important to consider carefully in advance is multi-cloud deployments.
According to Gartner, the best strategy is to “choose a primary, preferred provider, and then when the organization has business requirements that the provider cannot meet, add additional providers in an orderly fashion driven by specific business needs.”
Prioritize resilience
Utilize strategies such as distributed cloud services to ensure that customers can continue to access your services even if an issue arises with a specific server or provider.
Train your own talent
Skilled IT professionals are hard to find, so it could make sense to train your own talent. Start with your current IT team to find out if anyone would like to build their skills in cloud deployment.
But don’t overlook other teams. Who knows, you might have a budding developer working in marketing or HR.
Where BairesDev Fits In
BairesDev helps enterprises design and execute practical cloud strategies, from single-cloud migrations to multi-cloud and hybrid architectures. Our teams combine cloud architecture, security, and automation expertise to:
- Modernize legacy systems onto AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud without disrupting core operations.
- Implement automation and observability so cloud environments are easier to manage at scale.
- Build cloud-native applications and data platforms that support AI, analytics, and future growth.
That lets technology leaders move from tactical cloud adoption to using the cloud as a foundation for how the business runs and grows.
Using the Cloud as a Foundation for Growth
Done well, the cloud can speed up product launches, sharpen decisions, and open new paths for AI-driven innovation.
As the cloud computing industry matures, decision-makers must balance agility with control. They need to evaluate which cloud technologies best serve their strategic goals, whether that means consolidating systems for efficiency, expanding into multi-cloud environments, or experimenting with emerging technologies like quantum computing.
The winners will be companies that stop treating the cloud as a stopgap tool and start using it as a foundation for how they work and grow.





