Back in the early 1980s, Nobel Prize–winning physicist Richard Feynman questioned whether traditional computers could ever truly model the complexity of quantum physics. At the time, the consensus was “not with the machines we have.” That skepticism sparked decades of research that slowly opened the door to what we now call quantum computing.
Fast-forward to today, and the technology is gradually moving beyond theory toward specialized, real-world uses, holding promise for advances in areas from cutting-edge materials science to secure global communications.
While quantum physics might sound purely theoretical, it’s a real branch of science that already shapes our lives. Lasers, transistors, and most of modern electronics exist because of quantum theory.
The possibilities extend far beyond: optimizing logistics, accelerating drug discovery, advancing financial modeling, improving climate predictions, and strengthening cybersecurity — areas where even supercomputers hit performance limits.
At BairesDev, we track disruptive technologies closely. In this article, we’ll break down what quantum computing is, how it relates to classical computing, where it’s headed, and how soon it might move from labs to business reality.
Quantum Computing in Context
Quantum computing applies the principles of quantum mechanics — the science of particles smaller than atoms — to process information.
Traditional machines use bits that represent 0 or 1. Quantum systems use qubits, which can exist in multiple states at once (superposition) and affect each other through entanglement.
The real power isn’t just faster processing, it’s the ability to evaluate many possibilities simultaneously. That is what truly sets quantum computing apart from classical computing.
One common measure of capability is quantum volume, which takes into account qubit count, connectivity, and error rates.
Quantum Advantage
Quantum computers are built very differently from classical computers. Instead of CPUs and RAM, they rely on quantum circuits, which use quantum gates to manipulate qubits.
Maintaining these delicate states requires extreme conditions, such as superconducting circuits cooled near absolute zero or trapped-ion setups shielded from environmental interference. All this makes quantum computing hardware complex, delicate, and prohibitively expensive.
The differences don’t stop with hardware.
Programming quantum machines is nothing like coding in Java or Python. They run specialized algorithms and lack the memory/processor architecture of conventional computers. Because of their complexity, quantum systems aren’t built for consumer markets. They are intended for enterprise, scientific, healthcare, and advanced technology sectors.
Where Quantum Computing Can Impact Business
Although much of the field is still experimental, real-world applications of quantum computing are emerging:
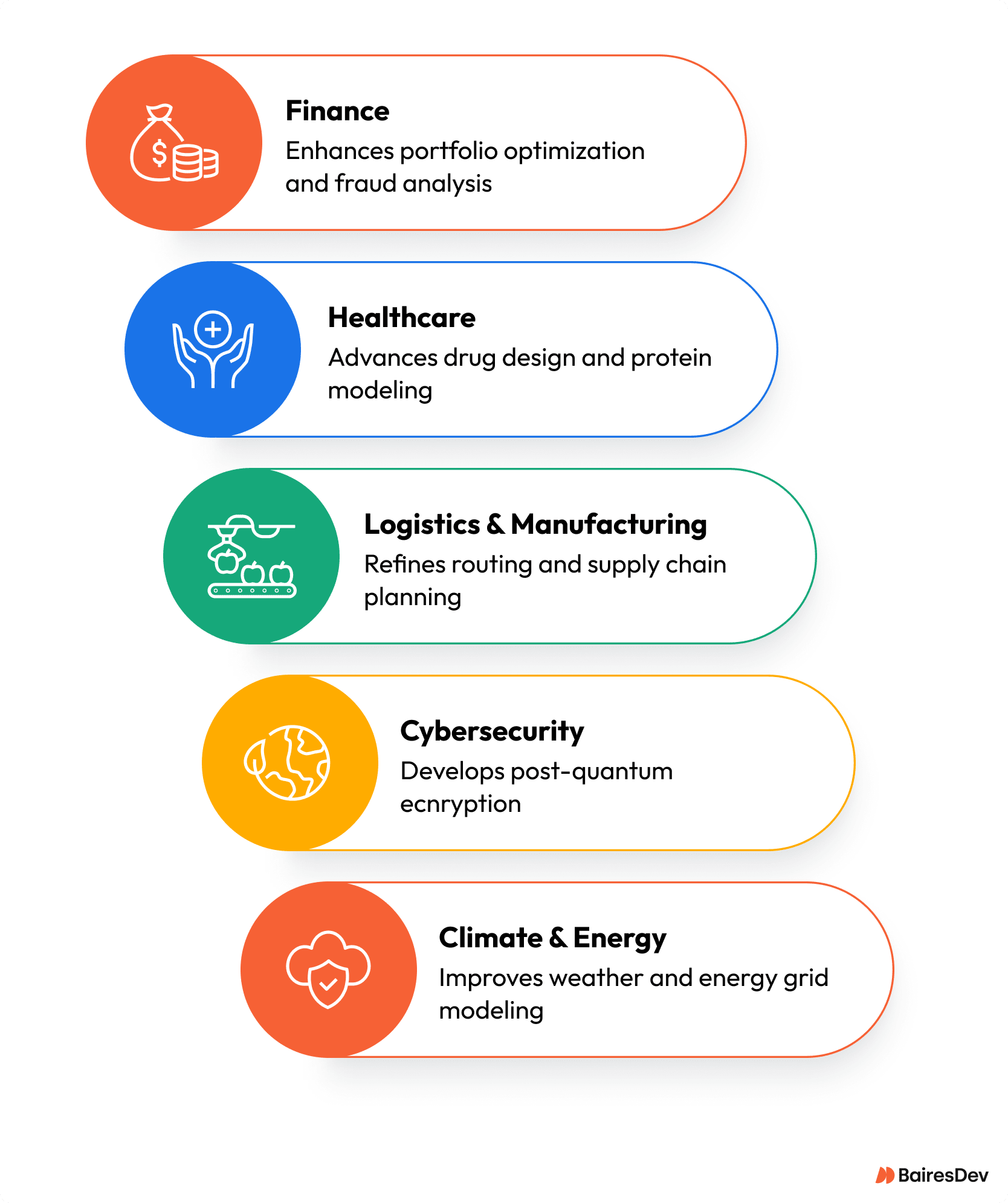
- Finance – Portfolio optimization, fraud analysis, and Monte Carlo simulations could run faster and with greater precision.
- Healthcare – Drug design and protein modeling may get a boost from ultra-precise molecular simulations.
- Logistics & Manufacturing – Quantum algorithms can refine routing, scheduling, and supply chain planning.
- Cybersecurity – Post-quantum encryption will be vital as quantum algorithms begin to challenge current cryptographic systems.
- Climate & Energy – Improved modeling of weather, energy grids, and carbon capture techniques.
The Challenges of Current Quantum Computers
Current quantum computers are extremely delicate. They depend on superconductors, Josephson junctions, and ultra-clean environments to operate without errors.
Physical qubits can only run for brief intervals and must be shielded from outside interference. Linking quantum processors into larger networks is another technical roadblock.
Quantum software is just as difficult to master. Tools like IBM’s Qiskit SDK are essential for writing algorithms that unlock real quantum advantage, and the industry still has a long way to go before development for quantum systems matures.
Scientific American states, “More research should bring us closer to advanced quantum technologies and the grandest goal of quantum information science, creating a fault-tolerant quantum computer that can indefinitely compute without errors.”
Quantum Networking
Another area of potential is quantum networking, which uses quantum key distribution for ultra-secure communications — a big consideration for industries with strict compliance requirements, as well as governments and defense applications.
As ZDNet notes, “The implications for a computing network where quantum processing plays a role, are enormous: hurricane models that account for every water molecule; global warming models that pinpoint next year’s forest fires; pandemic models that ascertain which species of bat when consumed and under what conditions, produce future coronaviruses.”
How Quantum Computers Could Change the Industry
Traditional computers are built to give you one clear answer. Quantum computers work in probabilities, which makes them better for problems where there isn’t a single obvious solution.
They will be used for different tasks, such as solving highly complex problems in much less time than with current supercomputers.
Still, quantum technology could bring new processes to traditional computing, science, industry, and many aspects of modern life:
- While quantum computers could potentially defeat many of today’s encryption techniques, they will also be able to create new ones that will be much more secure.
- Quantum systems excel at solving high-dimensional optimization problems, such as dynamic supply chain rebalancing, real-time fleet routing across global hubs, or minimizing risk exposure in complex financial portfolios.
- Contrary to what you might think, quantum computers will use less electricity than traditional computers. Trapped ion qubits, which use the electronic states of charged ions confined by electromagnetic fields, are one example of how quantum gate operations can be performed efficiently.
Business Application
One of the clearest early applications is in drug discovery. Traditional computers struggle to model the behavior of complex molecules, often requiring approximations that slow down research and impact accuracy.
Quantum computation can simulate molecular interactions at the quantum level, giving pharmaceutical companies a way to predict how new compounds will behave before costly lab work begins. This could cut years off development cycles and significantly reduce R&D costs, while also accelerating breakthroughs in areas like cancer treatment and vaccine design.
When Will Quantum Computing Become Mainstream?
Quantum computing won’t follow the same path as personal computers. It won’t end up on every desk, but will instead transform specific industries where classical systems hit limits.
At the core is the quantum processor — the equivalent of a CPU, but built to manipulate qubits rather than bits. These are still in early development, with researchers exploring topological qubits for greater stability and lower error rates.
Tech giants like IBM, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon are investing heavily in both hardware and cloud-based access to quantum environments, shifting the field toward commercial reality.
Governments are also investing. For example, the U.S. Department of Energy launched five National Quantum Information Science Research Centers under the National Quantum Initiative Act, dedicating $625 million over five years to push the field forward.
These efforts focus on advancing quantum devices that leverage quantum mechanical phenomena for applications such as breaking existing encryption schemes, simulating complex physical systems, and enabling new classes of secure communication.
For business leaders, the takeaway is clear: quantum won’t replace existing IT systems, but its specialized capabilities will be game-changing in the right contexts. Companies that prepare early will have an advantage when the technology matures.
What’s The Future For Quantum Algorithms?
Quantum systems have the potential to revolutionize computing. Superconducting qubits allow for the manipulation of quantum information through microwave photons. Classical physics, which governs macroscopic objects, falls short in explaining the phenomena observed in quantum mechanics.
Quantum advantage — the point at which quantum computers outperform classical systems for practical problems — is already being demonstrated in narrow contexts. The next breakthroughs will likely come from algorithmic innovation as much as from hardware improvements.
For technology leaders, the opportunity is now: start training teams, mapping data strategies, and exploring security upgrades so your organization is ready when business use cases align with quantum capability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What business problems are most likely to see an early return from quantum computing?
Problems that involve large-scale optimization, high-fidelity simulation, or complex statistical modeling are prime candidates. Examples include supply chain route planning, molecular design in pharmaceuticals, and risk modeling in finance.
How should we start building quantum capability without overspending?
Use cloud-based quantum services from established vendors for experimentation. Identify one or two high-value use cases, develop proof-of-concepts, and build internal literacy. Avoid premature hardware investment. Focus on understanding where quantum fits into your current technology stack.
What’s the realistic timeline before quantum affects enterprise security?
Most experts expect certain cryptographic algorithms to be at risk within the next 10–15 years. Migration to quantum-safe encryption should begin well before that. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is already finalizing post-quantum cryptography standards.
How do we measure progress in quantum readiness?
Key indicators include: documented quantum-relevant use cases, staff trained in quantum concepts and tools, vendor relationships in place, and a roadmap for integrating quantum-safe security.