Product managers (PdMs) and project managers (PMs) often work side by side, and their roles are often misinterpreted and mixed up, even in professional circles. However, their roles serve distinct purposes. The product manager’s role is strategic. Project managers focus on delivery, so their role is more tactical in nature.
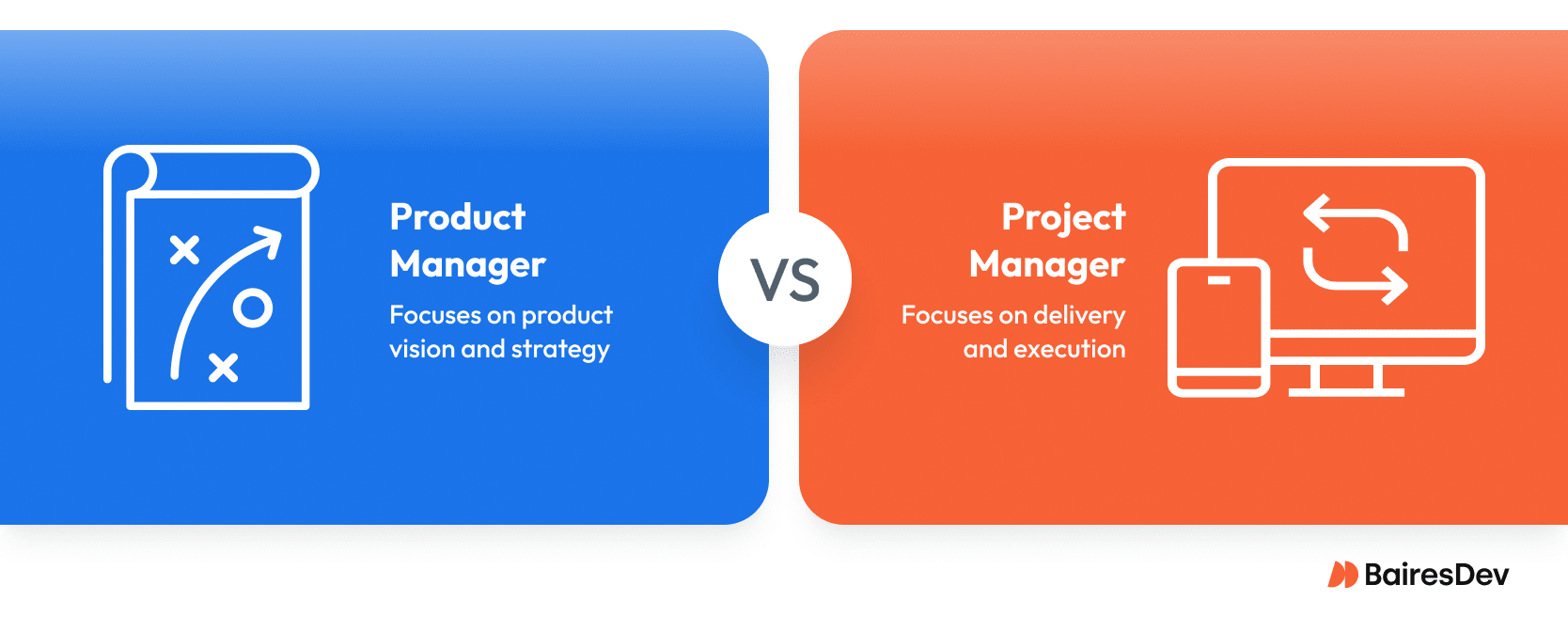
Let’s put it like this. The product manager focuses on high-level tasks, defining product direction, understanding customer needs, and aligning development with strategic business goals. The project manager makes sure everything is delivered on time, on budget, and within the project scope.
Let’s break down the key differences and see how they work together.
What Does a Product Manager Do?
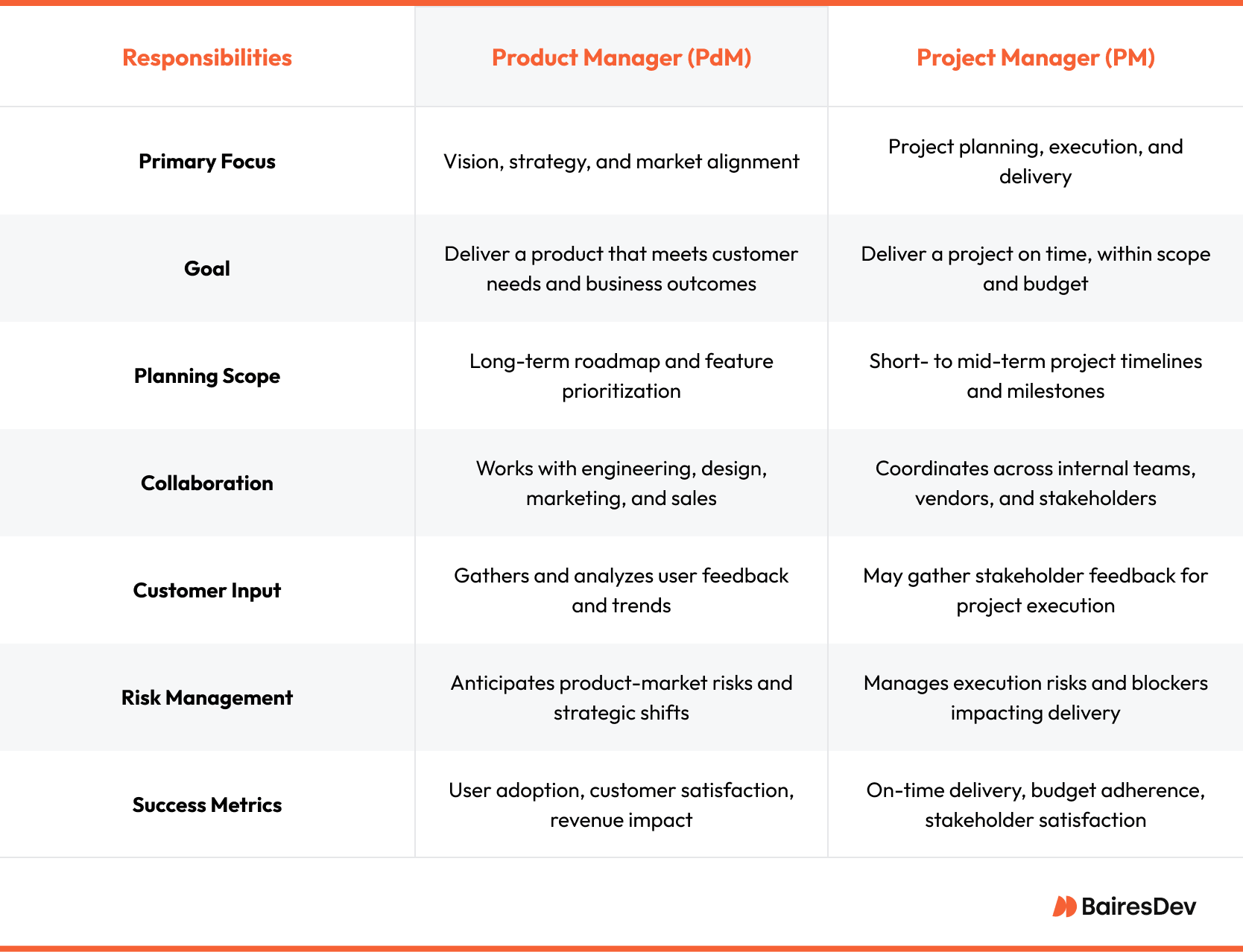
A product manager oversees the product’s entire lifecycle from concept to launch. They define what should be built and why. Their decisions are based on strategic objectives and backed up by customer feedback and market research.
Product managers work with engineering, design, marketing, and sales teams to translate strategy into execution. They make sure the product delivers value to the customers and the business. development and long-term success.
Key Responsibilities of a Product Manager
Product managers guide product development from initial concept to delivery, and beyond if necessary. Their main responsibilities include defining the product vision, prioritize development, and ensure alignment. This requires a lot of cross-functional collaboration and a wide range of skills, but we’ll get to the skill set later.
Product Vision and Strategy
A PdM maintains a clear vision of the product that aligns with the company’s goals, market opportunities, and customer needs. PdMs set long-term objectives and evolve the product strategy based on shifting market trends, business priorities, customer behavior, and other factors.
User Research and Feedback
Product managers continuously gather and analyze feedback through surveys, market research, and customer interviews. A lot of work is necessary to get a bird’s-eye view of the product and identify pain points. This research lays the groundwork for successful product management and helps focus the product on customer demands, delivering real value.
Roadmap Creation
Product managers create and manage the product roadmap by balancing short-term deliverables with long-term goals. Aligning the roadmap with internal resources and release timelines involves collaboration with cross-functional teams from engineering, design, and marketing. Keeping the roadmap up to date is another challenge. The roadmap has to be a living document, always adapting to new requirements and changes in the business trajectory.
All this requires a fair amount of knowledge and experience. So what about the skill set?
Product Manager Skills and Qualifications
Successful product managers need a blend of technical knowledge, strategic thinking, and strong leadership skills. They are positioned at the intersection of business, technology, and user experience and have no choice but to wear many hats.
Technical Expertise
Product managers aren’t expected to refactor code or design UIs, but they have to understand what makes their products tick. Familiarity with software architecture and technologies involved in the project facilitates effective communication with engineering teams. They need to know what’s possible and how long it will take. If a PdM lacks technical fluency, a lot of time could be lost in translation.
Leadership and Communication Skills
Product managers continuously communicate with stakeholders, including executives, developers, marketers, and customers, keeping everyone on the same page. They need strong leadership and communication skills to unite teams around a shared goal. Technical skill and business knowledge aren’t of much use if managers can’t articulate the big picture and steer teams in the right direction.
Strategic Insight and Research Skills
Product managers keep track of market trends, competitor offerings, and customer data to make informed decisions. They identify opportunities for product differentiation and adjust product strategy to align with evolving requirements and stay ahead of the competition.
What is a Project Manager?
A project manager is responsible for planning and execution. They operate within constraints, such as time, budget, and scope. Their focus is on how work gets done. Project managers turn strategic objectives into actionable plans by aligning resources and ensuring timely delivery.
Project managers coordinate teams, oversee tasks, monitor progress, and address blockers. They act as a central point of accountability.
Key Responsibilities of a Project Manager
Project managers keep projects running smoothly and align them with strategy. Their responsibilities usually involve:
Project Planning and Scheduling
Project managers develop comprehensive plans outlining objectives, timelines, tasks, milestones, and deliverables. Project management tools are essential in planning and execution, facilitating task delegation, progress monitoring, and communication among team members. Project managers establish schedules, make sure milestones are met, and adjust plans to accommodate scope changes.
Resource Allocation and Budget Management
Efficient delivery depends on good resource management. Project managers assess resource availability, evaluate team capacity, allocate budgets, and distribute them to meet project demands. They also track expenditures and resource usage throughout the project to stay within budget.
Risk Management
Identifying and mitigating risks is a core function of project management. Managers proactively address potential issues to reduce disruption. Of course, no amount of planning can prevent unforeseen disruption. When issues arise, project managers have to act fast to realign teams and keep the project going.
Skills and Qualifications for Project Managers
Turning strategy into reality isn’t easy, and project managers need a broad mix of organizational, financial, and interpersonal skills:
Organizational and Planning Skills
Managing multiple projects and teams requires exceptional planning. Project managers have to be well-organized to stay on top of all issues at all times. They also have to create detailed plans, forecast potential issues, and coordinate across departments and functions.
Budget and Resource Management Skills
Managing project finances and resources requires a good understanding of budgeting principles. Project managers must track costs, manage expenses, and make difficult tradeoffs when necessary.
Risk Management Expertise
A good project manager is a proactive problem-solver. They identify risks early and develop mitigation plans before things go wrong, not after. When issues do arise, project managers have to think on their feet and adapt quickly.
Project managers often have a Project Management Professional (PMP) certification.
How do Product Managers and Project Managers Work Together?
While PMs and PdMs have different roles, their work often overlaps and they frequently collaborate. Understanding where their responsibilities intersect helps support project delivery and successful product outcomes.
Where Their Roles Intersect
Both roles often collaborate on scheduling, resource coordination, and stakeholder management tasks. For example, a product manager may define the features and goals of a new software product. The PM may create a detailed project plan to deliver the development process by a deadline. By working together, they fit the project timelines to the product roadmap.
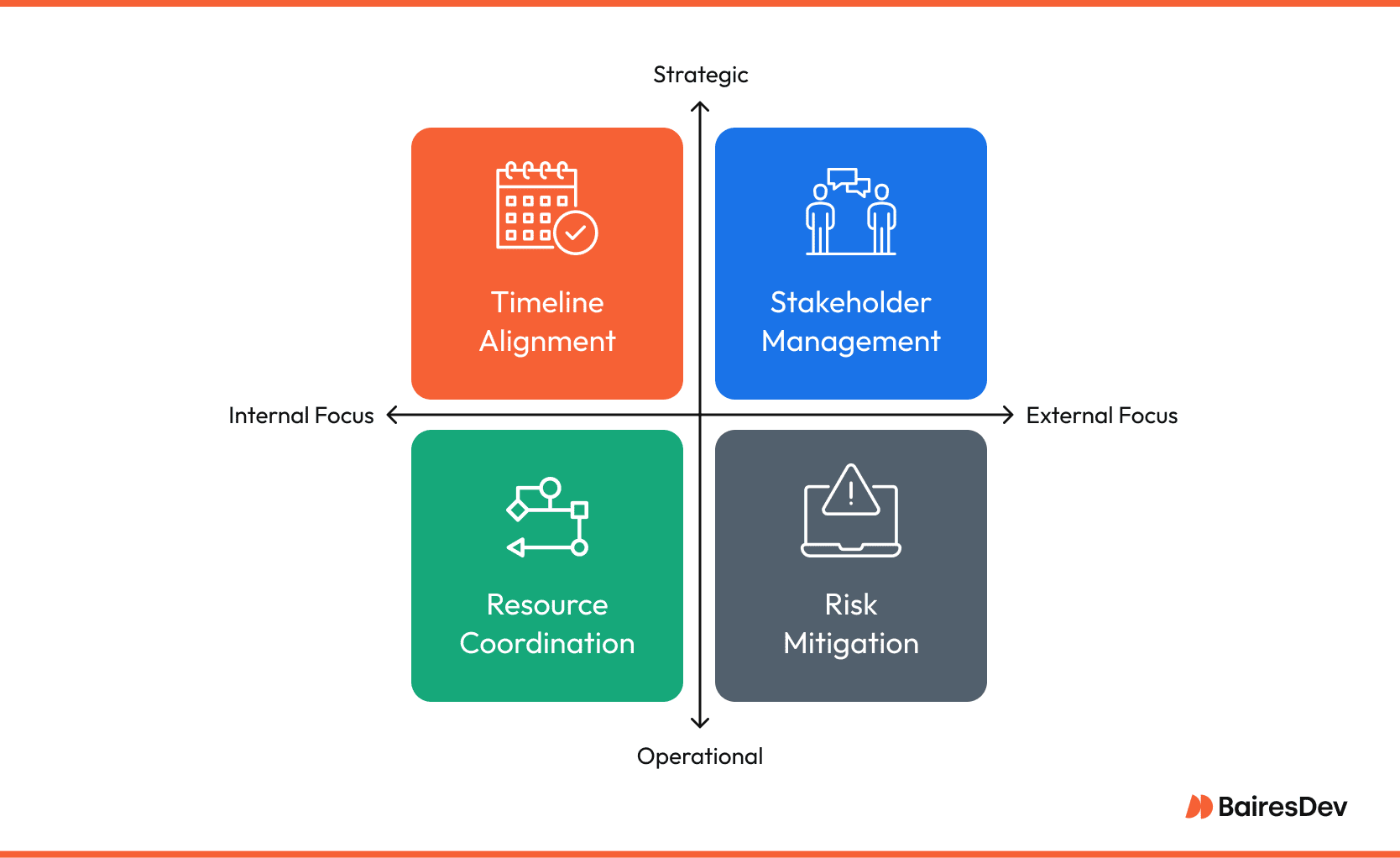
They also allocate resources to meet immediate project needs and long-term product goals. Project managers and product managers work together to mitigate risks. PMs manage project specific risks while the PdM may identify broader market risks that could impact the product’s success.
Challenges in Collaboration
Despite their alignment, collaboration can be tricky when product goals and project constraints conflict. For example, a product manager may add a new feature mid-project to enhance user experience. This can cause friction. PMs aim to protect the timeline and scope. Adding a new feature may cause delays or require additional resources.
Communication gaps can arise from the different focus of each role. Product managers are often concerned with strategic goals and long-term value, while project managers prioritise immediate deliverables. Regular check-ins and shared priorities can help bridge these gaps.
Should we Hire a Product or Project Manager? Or Both?
The decision to hire a product manager, a project manager, or both, depends on your business model, growth stage, and priorities.
Situations that Require a Product Manager
Product-led businesses often need product managers to guide product development and quickly adapt to market trends. They’ll benefit from managers who can define the product vision and strategy, engage with customers, and align marketing, design, and development teams around product goals.
Example: A company building a new SaaS platform may need a PdM to prioritise features based on customer feedback and competitive analysis.
Situations that Require a Project Manager
Organisations like marketing agencies or IT service providers are project-centric. They often emphasize project management and benefit from smooth execution. Delivering work on time and within budget is what matters. PMs make it happen. They manage resources, timelines, and make sure everything is on track.
Example: A digital agency creating marketing content for an e-commerce platform needs a project manager to ensure predictable delivery and meet deadlines.
When to Hire Both Roles
Businesses with complex products or projects often need both roles, especially software companies building products in an Agile environment. In larger organizations with structured project management, the product manager oversees the product strategy while the project manager ensures each phase of the development process is executed efficiently.
Example: An Agile scale-up working on multiple products can have a PdM driving the roadmap while PMs handle sprint planning, delivery, and resource management.
Having PMs and PdMs on the team can increase organizational efficiency and deliver better outcomes, making it easier to balance strategic and tactical objectives. The product manager can focus on the product vision and roadmap, while the project manager manages the day-to-day and keeps the team on track.
Improved Execution and Resource Allocation
The complementary nature of these roles helps companies plan and execute projects. Product managers handle long-term strategies, while project managers focus on immediate tasks that bring those strategies to life.
Both roles contribute to better resource management. Waste is reduced, cross-team collaboration is improved, allowing for greater efficiency.
Choosing Between Product Manager and Project Manager Careers
The choice between a career in product management or project management depends on your skills, strengths, interests, and career goals.
Personality and Skill Set Match
Product Manager: Ideal for strategic thinkers, user-focused, and market-driven. Product managers are good at understanding customer needs, shaping vision, setting long-term goals, and developing strategies. They need strong communication and collaboration skills as product managers work closely with cross-functional teams.
Project Manager: People who thrive in project management are often highly organized, detail-oriented, and skilled at execution. They enjoy planning, scheduling and meeting deadlines. They focus on project scope and budget. Problem solving and risk management skills are key as project managers navigate challenges to keep projects on track.
Career Paths and Progression
Product Management Career Path: Product managers can move up to Senior Product Manager, Group Product Manager, Director of Product, to Chief Product Officer (CPO). As they gain experience, they may take on more responsibility for larger products, lead multiple product teams, or oversee product portfolios across different markets.
Project Management Career Path: Project managers can move up to Program Manager, where they oversee multiple related projects, or advance to Director of Operations, where they manage broader organizational initiatives. Certifications like Project Management Professional (PMP) or Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) can enhance career prospects.
Salaries and Job Outlook
Salary Comparison: Salaries for PMs and PdMs vary by industry, location, and company size. Product managers earn slightly more on average due to their direct impact on revenue growth. Project managers also earn competitive salaries, especially in industries like IT.
Job Growth: Both roles are in high demand across sectors, as companies increase investment in digital initiatives and efficiency. Agile and digital transformation create additional opportunities.
Product and Project Managers: The Business Backbone
Product managers focus on a product’s long-term future while project managers focus on delivery and efficiency. Both are extremely valuable in modern businesses. Having the right person in each role improves operations, strategies, and outcomes.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a product manager and a project manager?
Product management is about a product’s lifecycle and long-term strategy, while project managers plan, execute, and deliver individual projects.
Can someone be both a product manager and a project manager?
Yes, some professionals take on hybrid roles combining product and project management, especially in smaller companies with limited resources.
Which role has more responsibility: product manager or project manager?
It depends on the organization. Product managers may have more strategic responsibility due to their impact on the product direction while project managers are responsible for delivering the project.
What skills do you need to be a product manager vs. a project manager?
Product managers need skills in market research, customer feedback analysis and strategic planning, while project managers need skills in project planning, risk management and resource allocation.
How do I choose between becoming a product manager or a project manager?
Consider your strengths and interests. Product management may be for you if you like working with long-term strategy and user needs. Project management might be more suitable if you enjoy planning and meeting deadlines.
Are both product managers and project managers required in small companies?
In smaller companies, one person may take on both or hybrid roles. As the company grows, defining these roles clearly can improve efficiency and outcomes, although some agile teams may continue to benefit from overlapping responsibilities.
Can a product manager work without a project manager and vice versa?
Yes, but it may be tough. Without product managers, product management suffers. Product managers may struggle with project execution, while project managers without product managers may lack strategic direction.






