Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) have shaken up the world of quality assurance (QA). A lot of companies are rushing to automate their testing because, let’s face it, automation speeds up development, reduces time to market, and cuts down on human error. But here’s the thing: despite all the buzz that “manual QA is dying,” that couldn’t be further from the truth. Manual QA is evolving, not disappearing.
QA engineers today are blending manual testing with automated tools and even AI and machine learning (ML) to boost their work. Sure, AI has made some incredible strides, but it’s not about to replace human judgment any time soon. Manual QA still plays a huge role in today’s tech world. In fact, the smartest approach is balancing manual and automated testing—that’s how companies stay competitive in this constantly changing industry.
While only five percent of organizations currently execute fully automated testing, surveys suggest that up to 73 percent of companies aim to achieve a manual-to-automation ratio of either 50:50 or 25:75. Here’s why.
Why Manual QA Matters
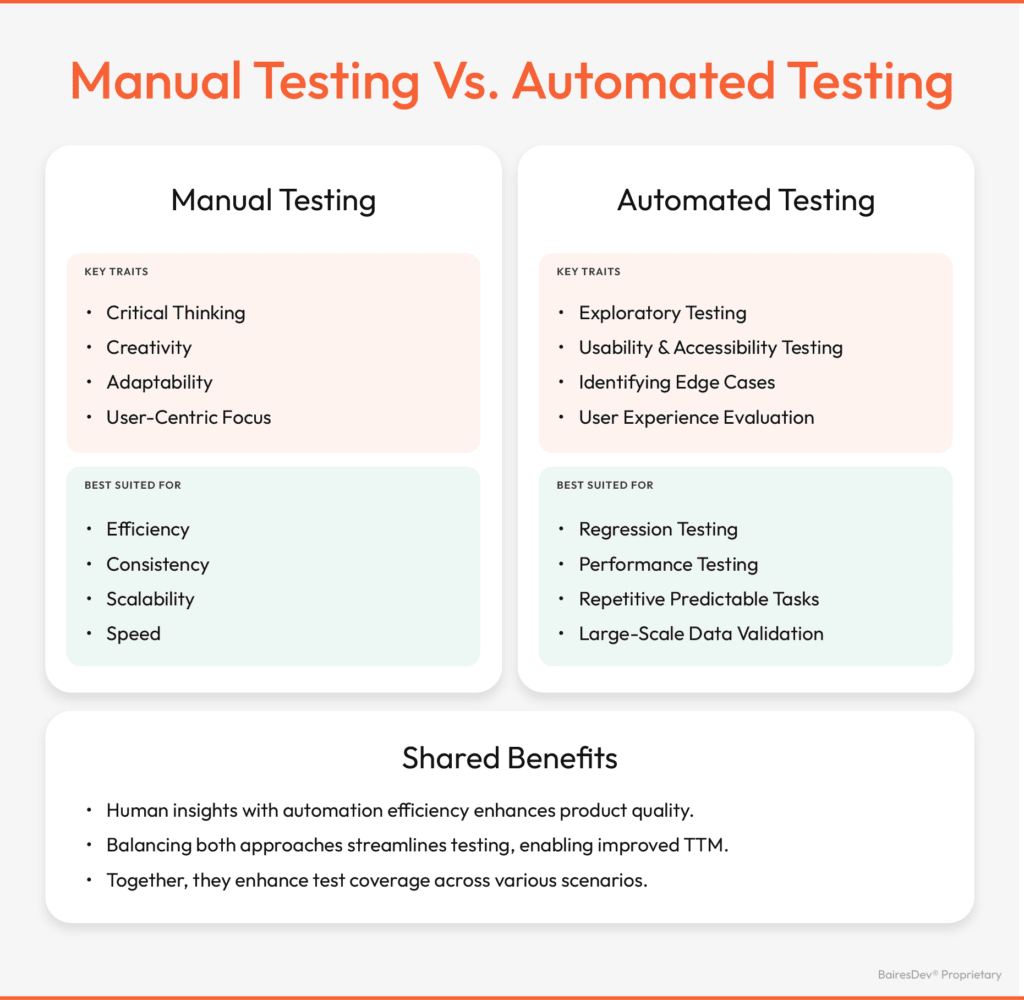
Manual QA brings something unique to the table that only humans can: critical thinking, creativity, adaptability, and a user-focused mindset. These are the qualities that let testers catch those subtle aspects of software quality that automated tools just can’t pick up.

Think about it like this: imagine testing a complex eCommerce platform. Sure, an automated script can confirm that the checkout button works, but a manual tester might notice that users with certain accessibility needs are having trouble with the process. That’s something automation would completely miss.
That example highlights why manual testers are still a crucial part of development. Here’s a closer look at some key reasons manual QA matters just as much as ever.
To Enhance the User Experience
Manual testers are essential for evaluating things like usability, accessibility, and the whole user experience. They’re testing the software the same way a user would. Sure, automation can check if a checkout button technically works, but only a manual tester can tell if that button is actually user-friendly, intuitive, and meets real user expectations. Does the button take you smoothly to the payment page? Does it load quickly? Is the navigation straightforward? Only a human can really answer those questions.
To Detect Real-World Issues
Real-world usage can bring out unexpected issues that only manual testing can uncover. That’s because human testers can reproduce complex scenarios that automated scripts might miss. This is especially true when dealing with edge cases, such as accessibility needs. It boils down to the fact that manual QA brings a greater focus to detail.
To Validate Requirements and Assumptions
While automation ensures that code runs as expected, human testers apply judgment to ensure the software aligns with user expectations and complies with regulations. A human could better determine whether or not the checkout process complies with regulations, such as the legalities surrounding taking users’ credit card information. QA testers also interact with developers, designers, architects, and project managers to ensure that the product is aligned with bigger-picture company goals.
To Anticipate Issues Before They Arise
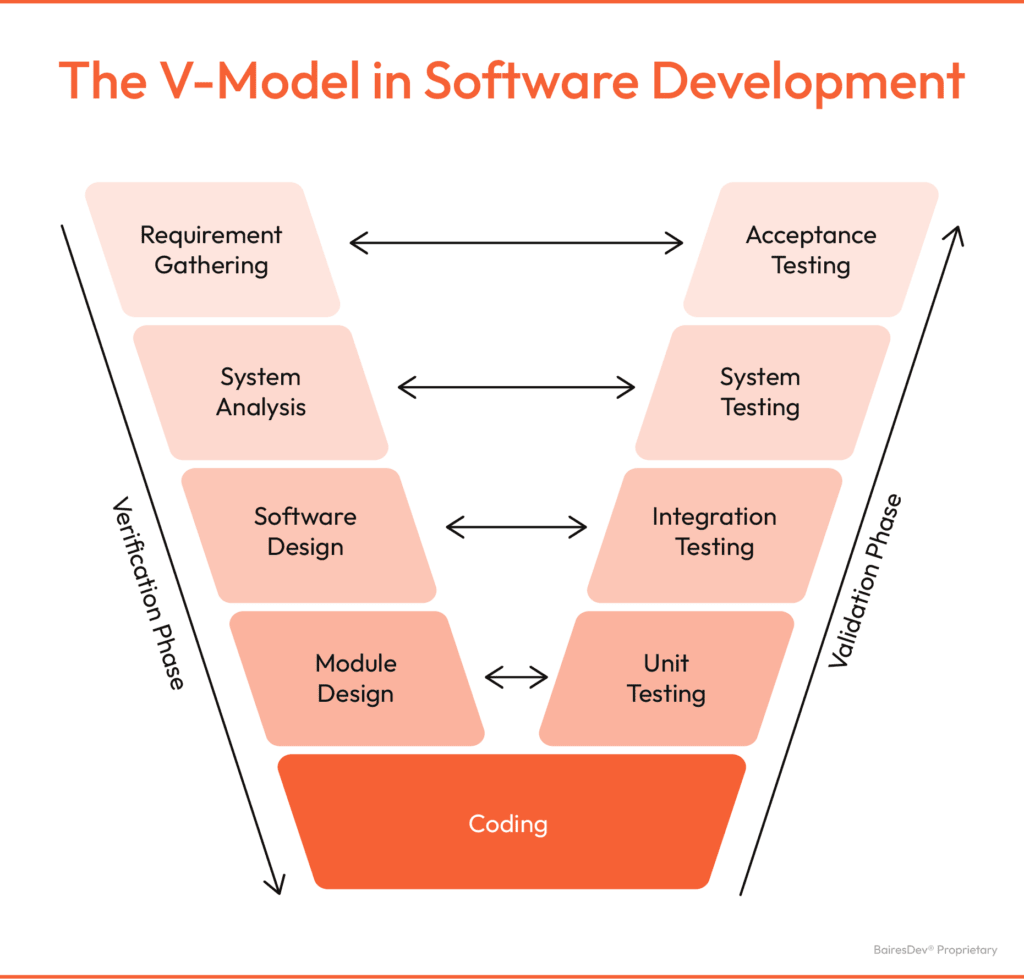
A QA engineer does more than just troubleshoot; they also work to prevent issues from happening in the first place. Through the V-model of software development, QA teams ensure quality at every stage of the project lifecycle, from initial requirements gathering to final deployment. For every stage of development, there’s a corresponding QA stage. This approach allows development teams to anticipate errors and scenarios every step of the way.
Manual QA helps ensure that software meets business goals and user expectations. Human testers provide insights that can influence the design, architecture, and functionality of the software, contributing to a more refined product. Their involvement ensures that issues related to usability, security, or performance are caught early, reducing costly fixes later in the development cycle.
Augmented Capabilities: Combining Automation and Manual QA
While manual testing is still essential, automation can complement manual QA. A balanced approach is best. But don’t just take our word for it. According to Deloitte’s 2023 Quality Engineering (QE) Trends Report, companies that integrate manual and automated testing see greater coverage and faster release cycles than those that only use manual techniques.
Automation can handle repetitive, predictable tasks. This might mean running test scripts across browsers, devices, or operating systems. Automated testing also excels at ensuring that code performs consistently under specific conditions and auto-generating test data.
And these automated tasks would free up time for manual testers to instead focus on scenarios that require more intuition and adaptability. Manual QA excels at addressing edge cases, conducting exploratory testing, and navigating creative scenarios.
For instance, an AI tool might automate regression tests for large-scale enterprise software. But the manual testers would still need to evaluate the user experience of new features being integrated into the product.
The Future of Manual QA in the Age of AI
AI is indeed reshaping how software testing is conducted. However, rather than replacing manual QA, it is empowering testers with advanced tools and capabilities. AI can automate complex testing scenarios, generate test cases based on application requirements, and even trigger tests within CI/CD pipelines in real time. But humans will always be necessary when it comes to building products for other humans.
AI tools are particularly useful in analyzing large datasets to detect patterns, identify anomalies, and uncover subtle defects that manual testers may miss. However, human testers remain critical in applying these insights, particularly when it comes to understanding the broader user experience. That’s why leveraging automated techniques can help to enhance manual QA and why leveraging human QA testers can help make the most of automated techniques.
Plus, manual QA professionals will increasingly collaborate with AI systems to enhance their effectiveness. But times are changing, which means that manual testers will need to develop skills in interpreting AI-generated results and maximizing their efficiencies. The future of QA will see manual testers evolving into strategic roles that ensure user-centric quality while utilizing AI to streamline more routine aspects of testing.
In Conclusion
Manual QA is far from obsolete. In fact, it plays an essential role in delivering high-quality software in today’s AI-driven world. While automation is transforming testing, manual QA remains irreplaceable for critical tasks like exploratory testing, user experience evaluation, and validating edge cases. Together, manual and automated testing form a comprehensive strategy that enhances overall software quality.
To explore how our Manual Testing Solutions can elevate your next project, contact us here.






