Some rivalries are so big they define entire industries. Godzilla vs. King Kong. Coke vs. Pepsi. And in the world of smartphones, iOS vs. Android. Since Apple launched the first iPhone back in 2007, the battle for supremacy has been on between these two.
Android vs. iOS isn’t just important for smartphone users, it’s a big decision for mobile app developers and the brands and businesses that hire them. In this post, we’ll look at the history of Android vs. iOS devices and which one you should use if you’re building third-party apps yourself.
Market share and user base
In the wider mobile operating system market, iOS and Android are the two biggest. We’ve compared their global and regional market share and user demographics.
Global market share comparison
iOS and Android combined make up 99% of the global mobile operating systems market. Since iOS only supports iPhone devices, Android has a much bigger chunk of this 90%; in 2024 70% of the global market share was Android, 28% was iPhone.
The Android vs. iOS debate gets more interesting when you look at regional variations. iOS has a stronger presence in developed markets; for example 70% in Japan, 60% in Denmark and Norway, more in the US. Android is stronger in emerging markets, but there are countries like the UK where it’s almost 50/50.
So, it’s very important to consider the market share in your country of origin if you’re deciding between iOS app development and developing for Android users.
User demographics
In addition to their market share, iOS and Android users have different demographics. It’s hard to apply demographic data globally as demographics vary by region. But in general, iPhone users are higher earners; this is because Apple devices are more expensive than Android devices. iOS has more ultra-high earners in general because of the premium devices offered by Apple.
Recent research also found that younger generations are more likely to be iPhone users, older generations more likely to have Android smartphones. Customer loyalty is high for either option; most people who are already iPhone users won’t switch to Android devices. So that’s a glimpse into the demographic differences involved in the Android vs. iOS debate.

User experience and interface design
One of the biggest differences between Android vs iOS is the UX (user experience) design of each of their operating systems and how their interfaces work. We’ve broken it down below.
iOS interface
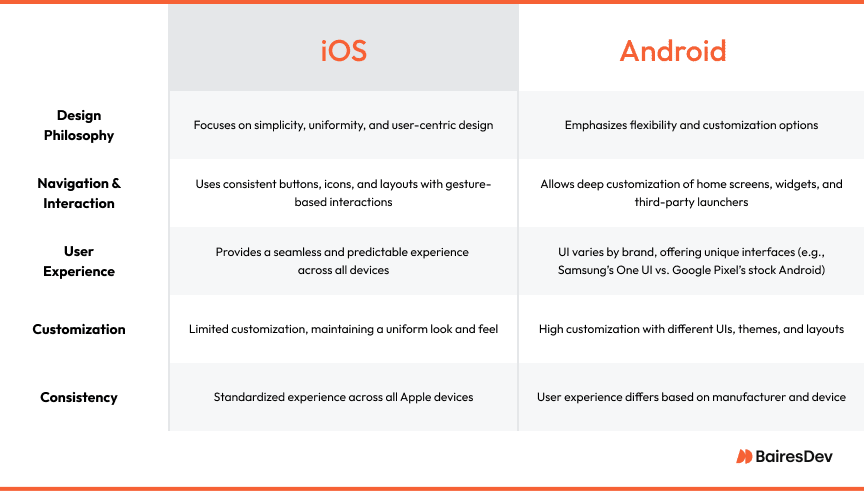
Since day one, Apple’s design philosophy has been about simplicity, uniformity and user centric design. They want to create intuitive and seamless experiences. This philosophy is reflected in the consistency across iOS apps where buttons, icons and layouts follow patterns, making it easy to navigate.
iOS also has gesture based interactions, users can swipe, pinch or tap for a more natural and fluid navigation experience. Navigation is streamlined through clear and predictable paths like tab bars and back buttons. This makes it easy for users to find what they need without feeling overwhelmed. This can be optimized further if developers follow mobile app design principles.
Android interface
Android is known for being a more free and flexible alternative to strict iOS design guidelines. Android’s interface is known for customization options, users can personalize their devices to their liking. Unlike iOS, Android also has deeper control over home screens, widgets and even third-party launchers so users can change the look and feel of their devices.
But this flexibility can lead to differences in UI across different brands, depending on the Android device you have. For example, Samsung’s One UI has a distinct design with rounded corners, one-handed navigation and additional features like Edge Panel. Google Pixel’s UI has a cleaner, more minimalistic design with focus on Google’s software experience like Google Assistant and a more “stock Android” feel. Where iPhone users know what to expect with the latest Apple devices, the Android OS can be quite different depending on the user.
Hardware
Maybe the biggest difference between Android vs iOS is the hardware they’re on. We’ve listed which devices have iOS and which run Android.
iOS hardware
Apple is very exclusive with iOS. If you hire iOS developers they can only create iOS apps and solutions for Apple devices, mainly iPhones which means a tight integration between hardware and software. This can be a advantage for iOS as an OS as it allows for consistency in design and better hardware-software integration.
By controlling both the hardware and the iOS OS Apple creates a streamlined ecosystem where the user experience is consistent across all iPhones.
Android hardware
Unlike iOS, Android is available on many different Android smartphones and devices. These Android phones are offered by multiple manufacturers like Samsung, Google and OnePlus among many others.
So there are more price points for Android phones depending on the manufacturer. This makes Android more accessible than iOS but also means there’s more variations in design and build quality of Android phones.
Performance and optimization
Each OS has its own performance and optimization. We compared both the optimization and app performance across Android vs iOS below.
OS optimization
iOS benefits from the tight integration between hardware and software as Apple designs both the OS and the device. This close relationship means iOS is highly optimized with better battery life and more consistent user experience across different iPhone models. Apple’s controlled environment also means faster updates so all devices get software updates and security patches on time.
Android operates in a more varied ecosystem. While this gives users more choices, it also means optimization challenges. Android device performance can vary greatly depending on processor power, RAM and device age. Device performance benchmark across Android devices shows more variation and some lower-end devices may have slower performance or less consistent performance. User feedback on Android devices reflects this diversity, higher-end devices like Google Pixel or Samsung Galaxy get praise for smooth performance while budget devices get criticism for lag or slower updates.
App performance
App performance and stability can vary greatly between iOS and Android mainly due to the difference in hardware and OS integration. iOS apps are more consistent and stable because Apple controls both the hardware and software; developers also have fewer variables to consider when building for iOS as the number of devices is limited and the hardware is standard.
Android apps may face performance and stability challenges due to the many devices, each with different hardware specifications, screen sizes and performance capabilities. This diversity makes it harder for developers to optimize their apps for all Android devices as testing and fine tuning is required for different manufacturers and models. Android’s open source nature also means more freedom for customization but this freedom can lead to more complexity when ensuring compatibility and performance across devices.
App ecosystem and availability
iOS and Android have separate app ecosystems; the Apple App Store and Google Play Store respectively. We explained how available each of these stores are and how the stores of each of these mobile operating system options work.
App Store (iOS)
The App Store is curated, Apple enforces strict quality control to make sure only apps that meet their standards are available to users. This includes app review process that assesses functionality, security and user experience.
Also, Apple has app exclusivity, some apps or features launch first on iOS before it’s available on Android. This gives iOS users early access to popular apps and innovations which often makes developers prioritize iOS development.
Google Play Store (Android)
Google Play Store has a huge number of apps, reflecting Android’s open ecosystem and the many devices it supports. Unlike Apple’s curated approach, Google Play allows more freedom for developers to publish apps with less restrictions.
This openness brings many types of apps and innovations but can sometimes result to lower quality apps or inconsistent user experience across devices. The Play Store’s accessibility however encourages more developers to create and distribute mobile apps for Android users.

Security and privacy
App store security and the overall security of each OS is part of their functionality. Since mobile devices handle so much sensitive data, we reviewed the security features of both iOS and Android smartphones.
iOS security
Apple prioritizes user privacy and security. They have App Tracking Transparency (ATT) which gives users control over which apps can track their activities across other apps and websites. This means users’ personal data is protected and they have more visibility on how their data is used.
iOS has a good security record, fewer malware attacks compared to other OS. This is due in part to Apple’s closed ecosystem, strict app review process and regular software updates which all helps to protect users from malware and security vulnerabilities.
Android security
Google has improved Android security in recent years with features like Google Play Protect which scans apps for malicious behavior and alerts users to potential risks. Play Protect also monitors app activity on a continuous basis.
However, Android device fragmentation can impact security updates. Unlike iOS’s uniformity, the many Android devices means security patches are delayed or inconsistent. This fragmentation can leave some devices vulnerable to security breaches if updates are not rolled out fast enough, a constant challenge for Google and device makers to maintain app store security. If you’re developing an Android app, make sure to hire Android developers with security expertise to tackle this issue.
Customization and personalization
Mobile devices are very personal objects that people use daily. We explained the customization options of Apple’s iOS and Android.
iOS customization
In general, there are limitations to iOS customizability through Apple’s iOS design guidelines. Apple made some changes to this; iOS 14+ allows users to add widgets to their home screen in various sizes so users can personalize their mobile device’s interface.
Despite these changes, iOS still doesn’t offer the same level of flexibility as Android in terms of overall customization. Apple’s approach is more uniform and streamlined user experience where functionality and design consistency takes priority over customization.
Android customization
Android has extensive customization options that allows Android mobile OS users to personalize their devices beyond basic wallpapers and icons. Users can change themes, install custom ROMs and adjust system level settings to change the look and feel of their devices.
Android also supports third party launchers which allows for a complete overhaul of the user interface. Tech-savvy users can even root their devices and unlock even more customization options like removing pre-installed apps or installing advanced system tweaks. These options make Android a powerful choice for those who want a high level of control over their device’s appearance and functionality.
Ecosystem and integration
iOS and Android are part of a bigger ecosystem, Apple’s suite of tools and solutions and Google’s G-Suite products respectively. When choosing between Android vs. iOS, consider how each of these ecosystems is integrated with each system’s official app store and smartphone interface below.
iOS ecosystem
Apple’s ecosystem is designed for seamless integration across their range of devices, Mac, iPad, Apple Watch and HomeKit enabled devices. This interconnectedness allows users to switch between devices easily.
AirDrop allows for file sharing between Apple devices and Handoff allows users to start something on one device and pick it up on another, like drafting an email on an iPhone and finishing it on a Mac. iCloud means your photos, documents and app data are synced across all Apple devices so you have the same experience wherever you are. This integrated ecosystem is a big plus for users who value the convenience and seamlessness of Apple’s products.
Android ecosystem
Google’s ecosystem is built around their core products like Google Drive, Gmail and Chrome which all work seamlessly across Android devices. Google Drive offers cloud storage and synchronization of documents, photos and files, Gmail is the central hub for communication and Chrome allows users to sync browsing history, tabs and bookmarks across devices.
One of Android’s advantage is its compatibility with a wide range of third party devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart TVs and wearables. This flexibility allows users to integrate their Android experience with various brands and devices, making it a more open ecosystem compared to Apple’s.
Cost and accessibility
Last but not least, access to iOS and Android differs in terms of cost. We’ve explained the difference between the cost of getting into Apple’s iOS and an Android smartphone.
iOS pricing
iPhones have always been a premium option compared to other devices. The initial cost of an iPhone is high and there are also additional costs like accessories and repairs that can add to this amount.
Apple does offer a few ways to offset this upfront cost like their trade-in programs and financing options. But it’s worth remembering that iPhones and iOS in general is a more expensive option compared to an Android smartphone.
Android pricing
Since Android is not limited to devices from a single company, there are more pricing options for Android phones. Companies like Samsung and Motorola offers budget Android phone options but also premium options that rivals the iPhone’s functionality.
This affordability is one of the reasons why Android has a bigger market share than iOS globally and especially in emerging markets.
Making a final decision
All in all, there are many differences to consider when deciding iOS vs. Android today. If you’re a user, consider your budget, how important customization is to you and what other devices you have at home.
If you’re a developer, apply this to your target audience. Think about what type of device your users will have and prioritize those devices during your development cycle. This way you can develop solutions that’s accessible to your audience but not limiting, you can still develop for both iOS and Android so you can reach as many smartphone users as possible.
FAQs
Which is better for gaming?
iOS has better performance optimization for games because of its hardware-software integration and more uniform device specifications. Each has subscription services like Apple Arcade and Google Play Pass with exclusive game libraries, Apple Arcade focuses on high-quality, ad-free games.
Which is more secure: iOS or Android?
iOS is generally more secure because of its closed ecosystem Android, with its open nature, can be more vulnerable to malware, especially on devices that don’t receive regular security updates. But Android’s Google Play Protect has security scanning and privacy features have improved on newer versions of the OS.
Which is better for developers: iOS or Android?
For developers, iOS has more streamlined development tools like Xcode and a more consistent app review process. Android has more flexibility with Android Studio and an open app store, but its fragmented device ecosystem makes optimization more complex. The best option usually depends on the developer’s experience.
Can I switch from iOS to Android (or vice versa) easily?
Switching between iOS and Android can be tricky because of differences in data handling, apps and system settings. Both platforms have tools to help transfer data (e.g. Move to iOS for iPhone to Android and Google Drive for Android to iOS) but some app data or settings may not transfer smoothly. Users may also need to manually reconfigure some settings and find equivalent apps on the new platform.
Which has better battery life?
Battery life varies across devices. Apple devices like the iPhone have a power management system that balances performance and battery usage. Android devices with different hardware configurations can have better or worse battery life depending on the device brand and version. Some brands like Samsung and OnePlus have custom optimizations that can improve battery life.







