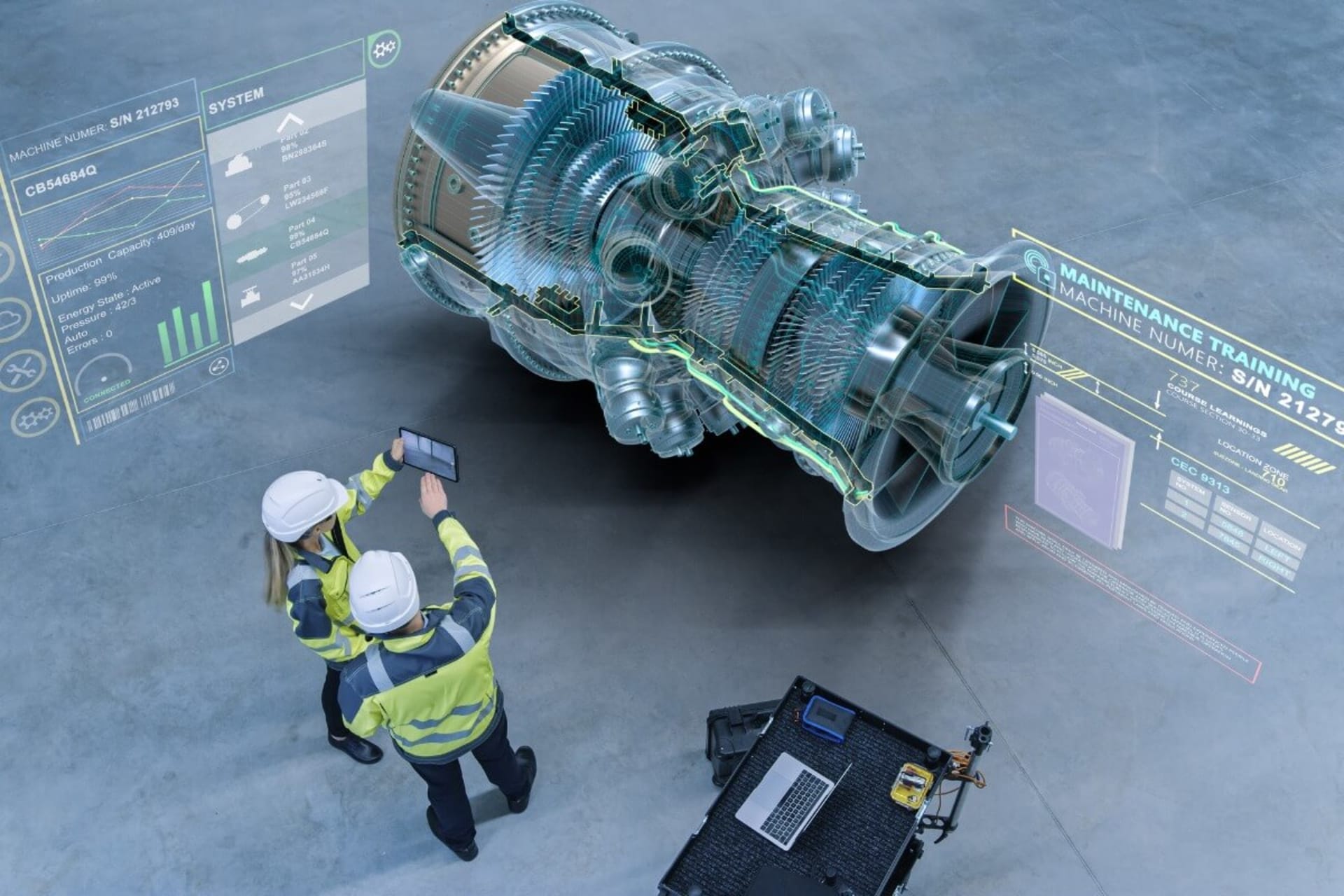
Walk onto a modern manufacturing floor today, and you’ll likely see more than just robots, CNC machines, and assembly lines. You might see an engineer wearing a sleek VR headset, reaching into a virtual environment to adjust a digital twin of a machine before any metal is cut. Down the aisle, a trainee runs through a safety training simulation, learning to handle a high-voltage system in a completely risk-free setting.

What once sounded like a tech demo at a trade show is now quietly transforming the manufacturing industry. Together, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), collectively known as extended reality (XR), are reshaping how manufacturers design products, train workers, optimize production, and reduce downtime.
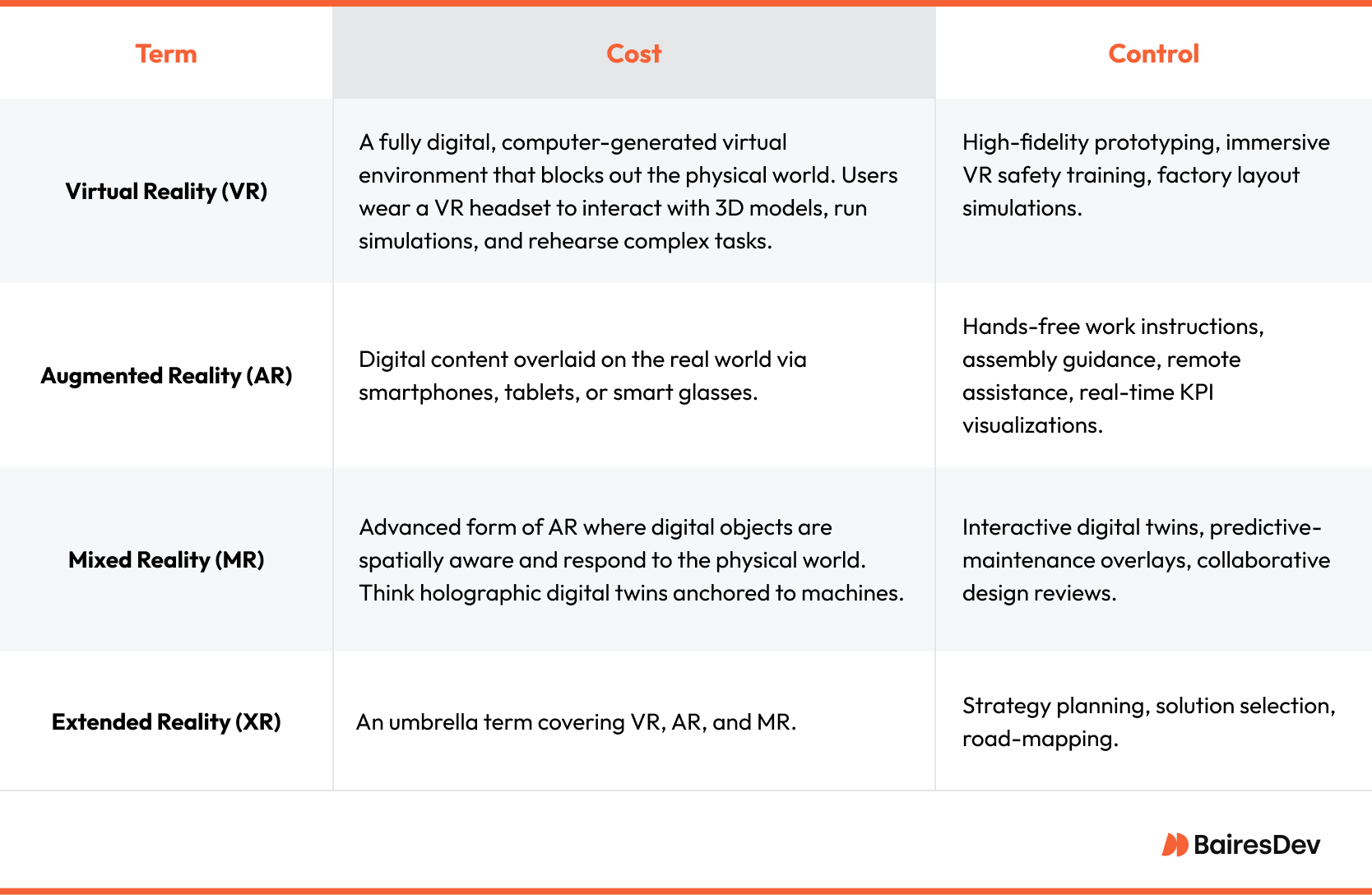
Let’s clarify these terms:
- VR fully immerses the user in a computer-generated space, cutting them off from the physical world. This is where manufacturers can create simulations, test different configurations, or train employees on new equipment without touching a single physical component.
- AR overlays digital data onto the real world. For example, projecting step-by-step assembly instructions on a machine via smart glasses.
- MR goes a step further, anchoring holograms to real-world objects so they interact dynamically. Think: a maintenance worker seeing a live, responsive hologram of an internal machine part overlaid on the real device.
ABI Research predicts that global spending on industrial XR will grow at an annual rate of over 18% through 2028, and the XR software/services market is expected to hit $300 billion by 2030, driven by rising demand for operational efficiency, labor safety, and smart factory integration. For VP-level decision-makers, XR is no longer an experimental playground. It’s a serious competitive lever.
Where VR and AR Deliver Enterprise Value
Where is this demand coming from, and where does XR technology fit into manufacturing?
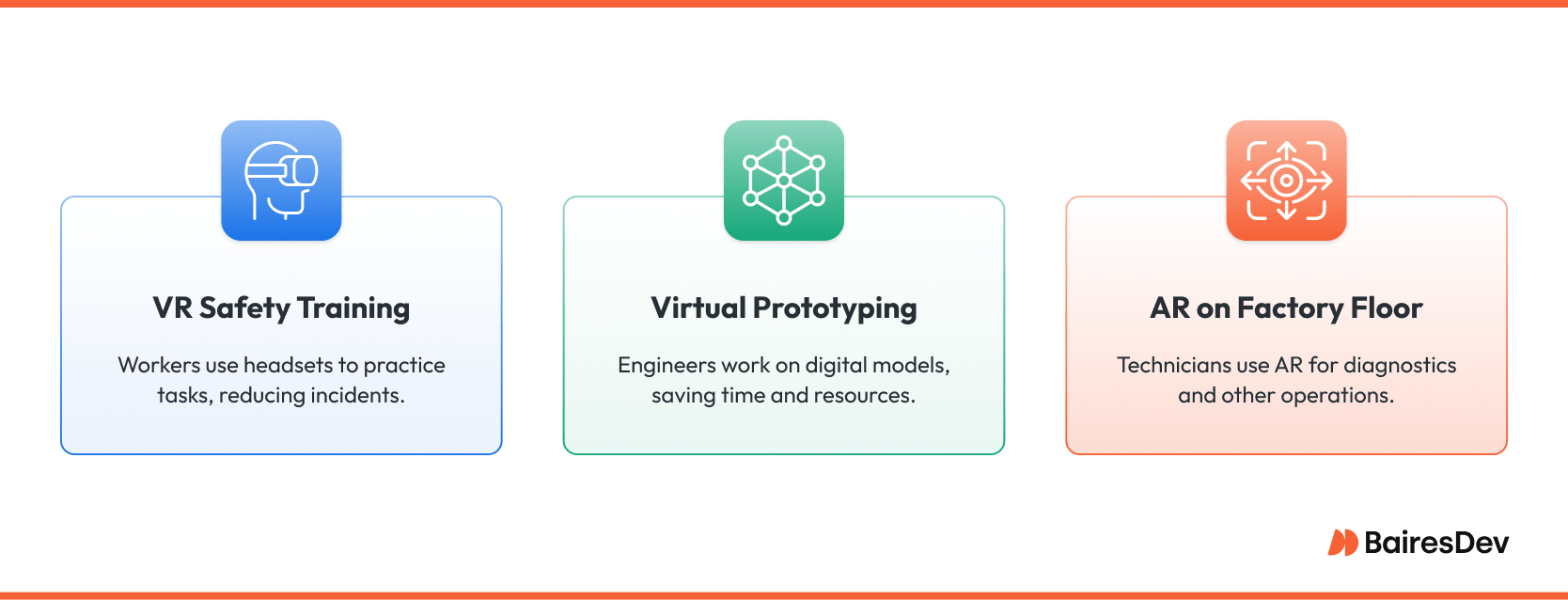
A Safer and Smarter to Train Employees
In manufacturing, VR safety training can be a game-changer. Traditional training programs and methods, such as manuals, videos, or even supervised practice, fall short when operators need to prepare for dangerous or rare events.
With VR, employees can rehearse high-stakes tasks like lock-out/tag-out, hazardous materials handling, or confined space entry in a controlled environment that feels real. They experience the sights, sounds, and even vibrations of the equipment, but without the risk.

Beyond safety, VR training boosts skill retention. Studies show people remember up to four times more from immersive experiences than from reading or watching alone. This is particularly critical when training new employees on complex equipment or processes, where mistakes can be costly.
Accelerating Design and Prototyping
Manufacturers typically invest significant time and money creating physical prototypes to test new products, tools, or line layouts. But a single full-scale engine test stand, for example, can cost $150,000 and take months to build.
With VR technology, teams can develop and test virtual models quickly, adjusting designs on the fly before committing to physical builds. Engineers can walk through the virtual environment, tweak designs, and run stress or ergonomic tests in real time.
Early adopters of XR tech solutions report product development timelines shrinking by two to four weeks per cycle, delivering faster time-to-market and millions in saved costs on large-scale programs.
Optimizing Production Processes and Maintenance
On the factory floor, time is money. VR tools and AR technology can help optimize every second.
Consider predictive maintenance. Traditionally, a technician might receive a vibration alert on an asset but have to dig through spreadsheets or dashboards to figure out what’s wrong. With AR or MR, they can walk up to the machine, and an overlay instantly highlights the problem, showing temperature gradients, fault histories, or recommended actions right in the technician’s field of view.
Beyond maintenance, VR lets teams simulate new production setups, test different configurations of equipment, and validate changeovers without disrupting live operations. Warehouses operations benefit, too. AR systems can guide assembly line workers and forklift operators with real-time data, reducing mis-picks, reclaiming floor space, and improving inventory accuracy.
Technical and Operational Considerations
Successfully rolling out virtual reality technology at an enterprise scale involves more than just plugging in a headset.
Latency and computing power are critical. Any delay over ~20 milliseconds between a user’s motion and what they see can cause discomfort or errors. Manufacturers address this by installing edge GPU servers on the factory LAN, streaming VR simulations over Wi-Fi 6E or private 5G networks.
Data management becomes a challenge when you’re handling terabytes of high-fidelity simulation data. Engineering and L&D teams now manage VR content the same way they manage software code: using version control, secure artifact repositories, and strict access governance to maintain a single source of truth across global teams.
Device fleet management is another overlooked but critical area. When you’re operating hundreds of headsets across multiple facilities, you need robust mobile device management (MDM) tools. These ensure that every VR headset is properly configured, regularly updated, and secure, including features like remote wipe, camera disablement in sensitive areas, and encryption for protecting proprietary manufacturing process data.
Cybersecurity cannot be an afterthought. Any XR system integrated into production systems must meet enterprise security standards (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II), encryption at rest, and integration with the company’s identity management systems.
Ergonomics also play a big role. After all, professionals may need to wear headsets for hours, all while working and communicating with their teams. Today’s headsets weigh under 400 grams, but prolonged use still requires smart scheduling. Many plants interleave immersive training with hands-on practice or break sessions into short blocks to avoid fatigue.
Quantifying Business Impact
When properly integrated in manufacturing, VR and AR generate tangible, trackable ROI.
- Prototyping cost savings: Replacing physical prototypes with virtual representations cuts material, labor, and lead time.
- Improved safety and quality: Immersive safety procedures and assembly training lower incident rates and boost first-pass yield. One consumer goods plant reported an 18% drop in defects after deploying VR rehearsals.
- Increased worker engagement: Investing in advanced, worker-centric immersive technology improves morale and retention, a critical factor in industries grappling with skilled-labor shortages.
- Sustainability gains: Remote design reviews and virtual showrooms eliminate travel, cut scrap, and support corporate ESG commitments.

Future-Proofing with XR
The next generation of XR tech promises even more. Headsets are becoming lighter, sharper, and more affordable. Edge-cloud architectures allow real-time interactive environments streamed across global networks. OpenXR standards mean that content developed today will run on tomorrow’s hardware without costly rewrites.
AI is playing a growing role, too. Generative design tools are now capable of automatically generating virtual reality simulations based on prompts like “12-second takt-time aluminum weld cell,” letting engineers tweak and deploy new simulations in hours instead of days.
Regulatory frameworks are also maturing. Europe’s Machinery Regulation and evolving OSHA guidelines are starting to address advanced technology training requirements, meaning companies investing now in auditable, data-logged VR systems will be better prepared for compliance demands down the road.
Choosing the Right Partner
A successful VR initiative hinges on the right partner. Industry knowledge is critical. Your vendor should understand the realities of the manufacturing environment, from takt times to PPAP requirements to compliance constraints.
Integration capabilities matter just as much. Does the partner know how to connect VR tools with your existing MES, PLM, or ERP platforms? Can they work with your IT team to deploy secure, scalable solutions across multiple sites? Security and governance must be built-in. Expect ISO certifications, role-based access controls, and device-level encryption, not as extras, but as core features.
Talent depth is also key. Effective VR solutions blend software engineering, 3D artistry, instructional design, and system integration. Nearshore teams offer the advantage of time-zone alignment, as async collaboration isn’t ideal (or possible) in manufacturing.
Getting Started with VR in Manufacturing
You don’t need to overhaul your entire operation to get value from VR. Start small. Pick one process — maybe a safety procedure, a changeover routine, or a high-defect task — and run a pilot. Four to six weeks is enough to test it.
Set clear metrics upfront. Track things like training time, incident rates, or first-pass yield. If the numbers move, you’ll know it’s working. Choose a partner who’s willing to tie their success to yours. Fixed-fee pilots and performance-based pricing show they’re serious.
Once you see results, scaling is easy. And in a business where every minute of downtime and every faulty part costs money, VR isn’t just cool tech. It’s a smart, strategic move.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How does VR improve worker safety in complex manufacturing environments?
VR allows manufacturers to train employees in a completely safe environment that accurately simulates real-world hazards. Workers can practice lock-out/tag-out, confined-space entry, or high-voltage operations without risk, reducing incidents and boosting retention of safety protocols.
How does VR support training on new or advanced manufacturing equipment?
VR enables workers to rehearse procedures on new machinery before it’s even installed. This approach builds confidence, reduces ramp-up time, and helps prevent damage or delays when the real equipment arrives.
What kind of ROI can we expect from immersive training programs?
ROI varies by use case, but companies often report faster onboarding, fewer quality issues, and improved safety metrics. For example, some see first-pass yield improvements of 10–20% after introducing VR-based work instructions.
Can VR integrate with the systems we already use in our manufacturing facilities?
Typically, yes. Modern VR platforms are built to connect with MES, ERP, and PLM systems, enabling real-time data visualization and traceable training outcomes. Integration ensures that immersive content is always in sync with what’s happening on the floor.
Is VR a good fit for multi-site or distributed manufacturing teams?
Absolutely. Virtual environments allow manufacturers to standardize training and process simulations across sites, ensuring consistency and reducing travel. Teams can collaborate in shared virtual spaces without ever leaving their facilities.