If you’re feeling pressured to cut costs through automation, you may be considering conversational UI. AI chatbots promise instant human-like interactions and fewer support interactions, and those stats would catch Satya Nadella’s attention on any QBR slide.
But let’s look at the intent. Too many teams rush to deploy conversational user interfaces, then run into the “invisible interface.” When customers don’t see the right cues or structure in a CUI, it’s hard for them to know how they should interact with it. Instead of delight, you get user frustration and higher support costs. In other words, the conventional wisdom about CUI doesn’t take growing pains into account.
This guide shows where CUI drives business benefits, and the steps product leaders can take to get there.
What Is Conversational UI?
Conversational UI is an interface layer that lets users interact with digital systems via human language. Users ask questions in a conversational way, often through messaging apps or voice assistants like Google Assistant. The CUI then uses natural language processing (NLP) to respond.
The tech started in the 1970s with basic interactive voice response (IVR). That’s the voice assistant tech that has likely frustrated you for decades in phone menus. Today’s large language models have upgraded that approach with context-aware chatbots. These automate and improve customer experience in ways traditional user interfaces can’t.
Well-architected CUIs flow like this:
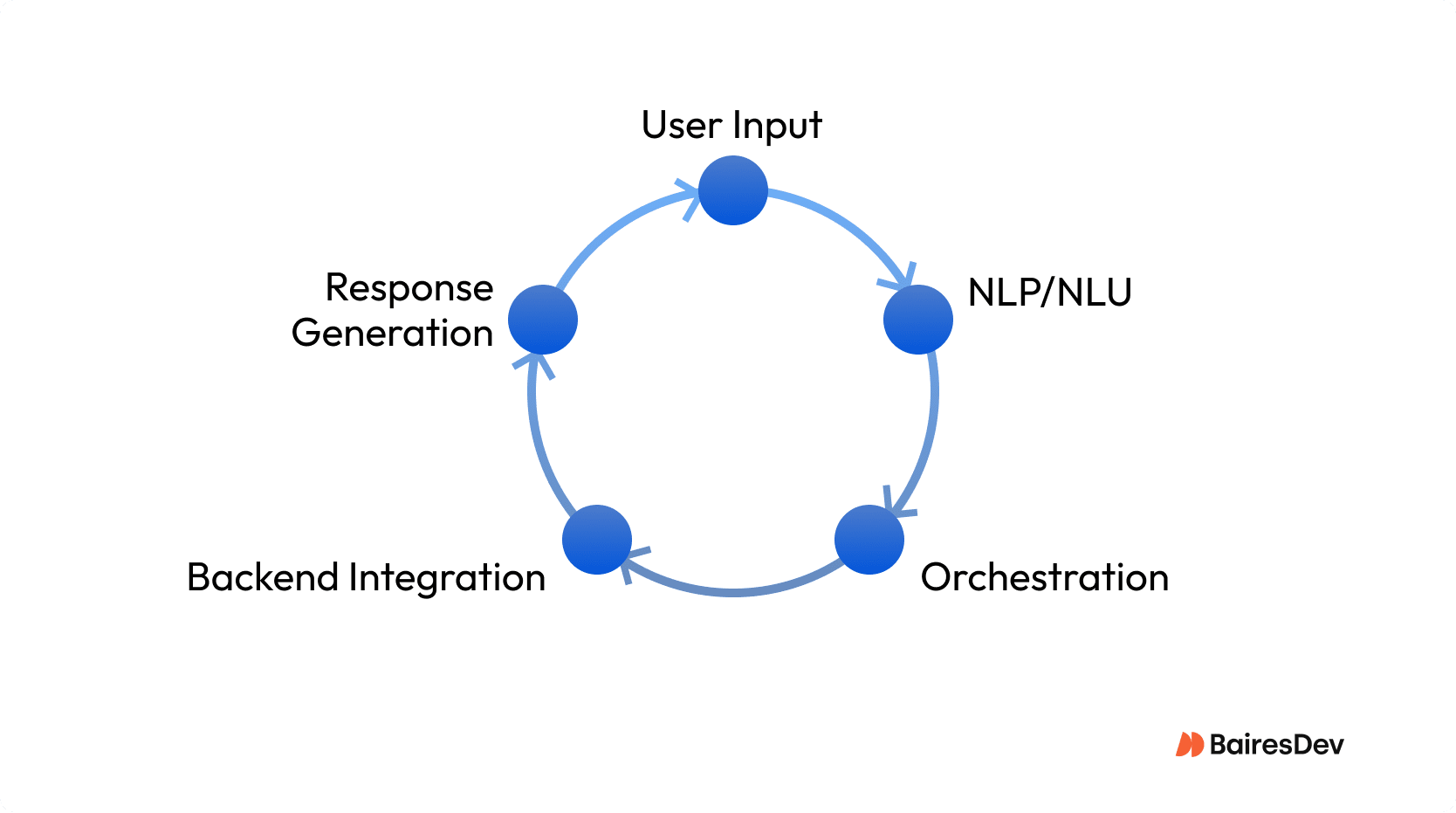
- User input: Captures human language via text or speech input fields.
- NLP/NLU: Translates messages into actionable intents.
- Orchestration: Dialog manager tracks conversation flow and manages context.
- Backend integration: Connects with APIs for data or action.
- Response generation: Crafts and delivers replies with reliability and speed top of mind.
Improved Engagement
Don’t be surprised to see onboarding rates climb when you start using conversational assistants. Users like how personalized touchpoints let them speak in their own way. For instance, an employee can request a benefits adjustment in plain terms.
This is the promise Adam Cheyer unlocked with his work on voice assistants. A “keep it conversational” ethos keeps users out of labyrinths of menu clicks. They ask once and get answers. That reduced friction turns every touchpoint into a brand moment.
Chatbots excel in situations like health check-ins and onboarding, where dialogue beats rigid GUIs. But edge cases are still problematical in some ways. Invisible UI traps can confuse and frustrate. Mixing conversation with visual cues can help keep even novice users on the happy path.
Persistent context and fast natural language understanding differentiate business-grade conversational UI deployments from shallow bolt-ons. Smart engineering creates intuitive platforms and keeps every engagement meaningful.
Scalability and 24/7 Support
Gartner reports that up to 80% of customer interactions can be automated with conversational apps. Cathy Pearl, author of Designing Voice User Interfaces, has consistently supported automation to scale support. The allure is instant answers and 24/7 reliability at much lower legacy costs than legacy systems.
| Factor | Conversational UI Impact | Traditional Human Support |
| Coverage (24/7) | Yes | Limited by agent shifts |
| Routine Inquiries Automated | 80% potential | 0% |
| Cost per Interaction | Fraction of human agent | High |
| Experience Consistency | High, when well-designed | Variable (training/fatigue) |
| Failure Mode | Confusion (“Sorry Wall”), LLM unpredictability | Hand-off/escalation paths |
Conversational UI Best Practices
Even subtle failures like NLP delays or dead-end flows can damage trust in an AI assistant. Intelligent bots need to adapt and hand off to a real person when needed. For example, when a healthcare portal bot fails to interpret a request like “cancel my appointment,” the user can end up in a frustrating loop of unhelpful responses. By redesigning the fallback logic to suggest likely next steps like “Talk to an agent,” engineering teams can turn a dead-end into trust. Here’s what to engineer for:
Design for Peak Loads
NLP latency hurts customer satisfaction with uncanny pauses. Distributed conversational UI architectures handle spikes without lag, so AI bots can respond in real time.
Map Fallback Paths
Edge cases break trust because they make users repeat themselves. Conversational UI best practices demand fallback orchestration and fast escalation to a real human. That’s especially important when virtual assistants fail to interpret voice commands.
Train After Launch
Intelligent bots need to be frequently retrained. Otherwise they miss user intent during high-value tasks. Update machine learning models often to reduce error message sprawl and improve accuracy.
Prioritize Discoverability
Blend hybrid conversational experiences and structured cues to help end users explore conversational manner workflows and find valuable insights free of dead ends.
Support Multiple Languages
Global user interfaces need natural language processing that handles multiple languages and their slang. In Mexico, a torta is a cake, but in Costa Rica, it’s a mess.
Preserve Context State
Maintain continuity across previous interactions and conversation flow. Persistent state enables personalized experiences, smooth schedule appointments, and automating routine tasks in a conversational manner.
Monitor Flow
Observability ensures reliability. Track conversation metrics, detect failure points, and tune natural language understanding to avoid “sorry walls” that frustrate users and increase customer service chatbots escalations.
Use Structured Logging
Structured logs uncover valuable insights. Capture human language input, state transitions, and latency events to strengthen artificial intelligence models and deliver reliable conversational interfaces at scale.
Common Pitfalls
Even production-ready conversational UI can break down under real-world use. Common failure modes include input ambiguity and misrouted intents. Engineering leaders must address these at the architecture level. That means designing for discoverability and context awareness while maintaining observability.
- Poor input design: Failing to constrain or guide user input causes ambiguous intents, breaking the flow and frustrating users.
- Brittle NLP models: Models trained on limited data often miss edge cases. Retraining with production logs improves coverage and reduces failure during high-value tasks like scheduling meetings.
- No escalation path: Without seamless transitions to agents, users get stuck. When bots fail silently, customer satisfaction drops and support costs rise.
- Static bot behavior: Rule based bots can’t adapt. They repeat unhelpful responses and can’t adjust to the same way users evolve their input over time.
- Lost context: Dropping session data mid-conversation ruins seamless experiences. Preserve conversation state to track past interactions and meet intent consistently.
- Lack of observability: Without structured logs and monitoring, teams miss failure signals. Visibility into conversation flows is critical for maintaining uptime.
Gathering Insights and Data
When teams invest in conversational UI, the upside is that every interaction generates authentic data that reveals intent and pain points along the customer journey. High-value analytics derived from natural language conversations spotlight where your users get stuck and what they search for.
Brands deploying artificial intelligence in CUIs can learn not just what users ask, but also when. They can capture everything from failed speech recognition attempts. Still, nothing good comes free. Privacy concerns abound as customers become more sensitive about conversational data collection. Customer trust is built with robust onboarding and transparent consent. Up-front data use explanations can further support this trust.
Checklist: What Engineering Teams Need for a Scalable Conversational UI Deployment
Building scalable conversational UI isn’t about just plugging in a bot and calling it a day. Tony Stark didn’t stop at JARVIS 1.0, either. Each layer needs to be robust and engineered for real-world complexity. Swivel-chair integration might solve today’s pain, but it won’t sustain tomorrow’s scale when users expect seamless transitions from smart speakers to web and mobile. Here’s what your engineering stack needs:
- Persistent session state: Tracks user input and context over multiple conversations for continuity.
- NLP vendor integration: Flexible connectors to leading large language models for improved intent recognition and multi-language support.
- Observability: Real-time tracking of performance and error rates. Ensures rapid triage when something fails.
- Human fallback paths: Built-in escalations for complex interaction. Users shift to a real agent instantly.
- Performance guardrails: Rate limits and api timeouts to manage load across high-traffic times.
- Dynamic onboarding: Clear cues for new users to minimize onboarding friction and accelerate adoption.
How Better Fallback Logic Fixed a Banking Bot
A major retail bank deployed a conversational UI on Facebook Messenger to help customers freeze or cancel cards. At launch, the experience fell short. Users typing “freeze my card” often triggered fallback responses like “Sorry, I didn’t get that,” even though the bot had relevant intents. NLP confidence thresholds were set too conservatively, and the fallback logic led nowhere. Without escalation options, users hit dead ends, abandoned the chat, and drove up call center traffic.
Engineering teams analyzed logs and discovered a pattern: NLP technology failed on edge phrasing (“block my debit”) or when users bundled time-consuming tasks in one message (e.g., “freeze my card and order a new one”). The fix involved two changes. First, instead of rejecting uncertain inputs, the bot surfaced likely intents as clickable options. Second, they added human escalation for ambiguous queries.
With structured logging and better observability, teams retrained the model, expanded synonyms, and adjusted thresholds. User flows improved immediately. Customers completed more self-service actions, the system scaled across languages, and support volume dropped.
This wasn’t about replacing humans. It was about meeting customer needs with less friction. A conversational UI works best when it guides, not guesses. In this case, what started as a broken flow turned into a channel that could play music, schedule appointments, or answer FAQs, without making users start over. For teams building or scaling digital assistants, this recovery story highlights the importance of treating fallback paths as part of the product, not a patch.