At CES 2025, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang laid out a bold vision: AI isn’t just about processing text anymore, it’s moving into the physical world. Physical AI understands movement, physics, and cause-and-effect relationships, making it a breakthrough for manufacturing. With AI powering robotics and machinery, factories are getting smarter, adapting in real time, and optimizing themselves like never before.
Smart factories have been evolving since the 2010s, but we’re now stepping into their next phase. These systems are about to rely on ambient intelligence, where sensors, AI models, and software create a seamless connection between the physical and digital worlds. Instead of reacting to problems, manufacturers can now predict and prevent them, making production faster, more resilient, and more cost-efficient.
What makes Physical AI stand out is its ability to see, plan, and act in dynamic environments. Take automotive manufacturing: AI-driven robots inspect car parts for defects, assist workers on the assembly line, and monitor machinery in real time, tracking temperature, wear, and performance. The result? Factories that self-optimize, anticipate future needs, and keep operations running at peak efficiency without waiting for humans to intervene.
How Ambient Intelligence Works in Manufacturing
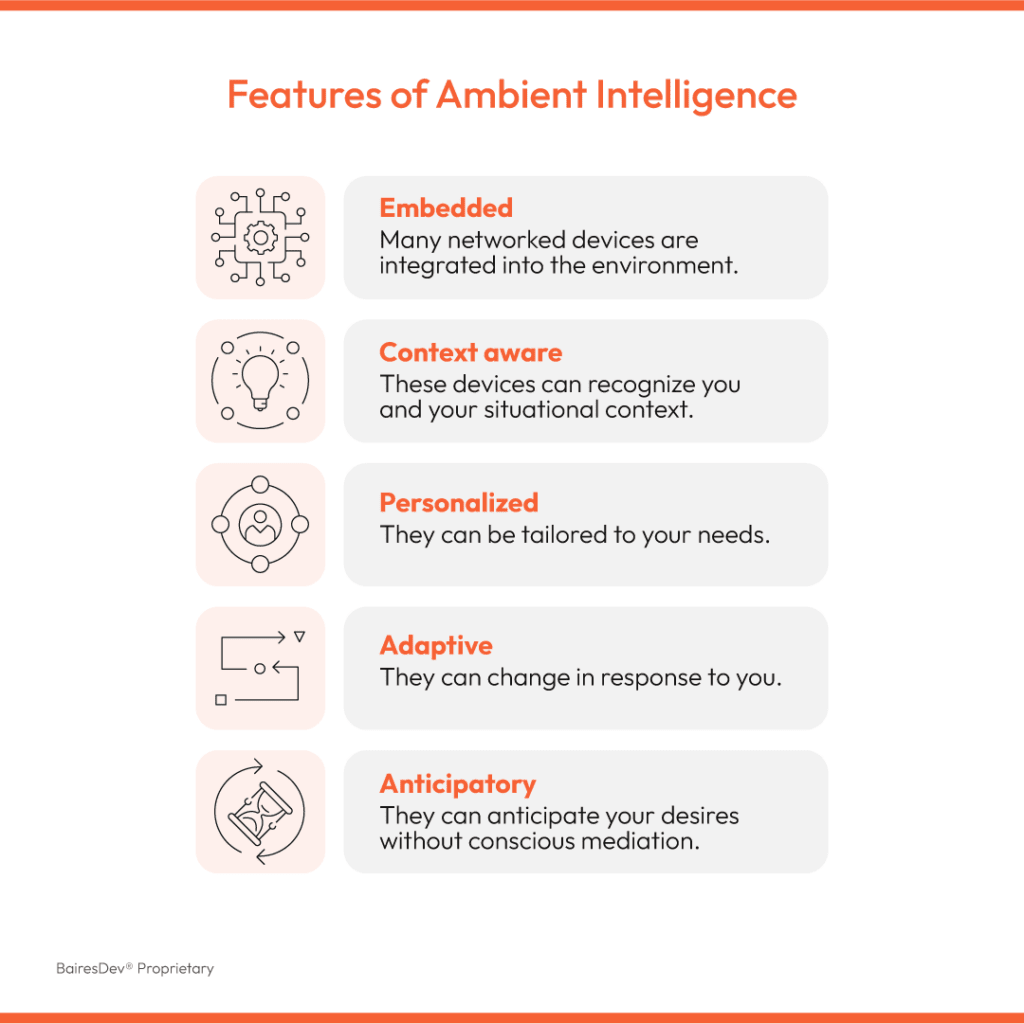
Ambient intelligence creates digital environments that adapt to people and their needs without requiring manual input. Unlike traditional automation (which follows predefined rules), AI-driven ambient intelligence predicts, optimizes, and manages operations autonomously. It learns, adapts, and refines processes in real time. Here’s a quick rundown of the core features of this technology.
So, what does that look like in manufacturing? Let’s illustrate some of its key features:
AI-Driven Perception
AI perception enables machines to interpret their surroundings using computer vision, sensors, and machine learning. These systems can identify objects, detect patterns, and flag anomalies. But while they’re excellent at recognizing details, they don’t inherently understand context. That’s where deeper AI models come in.
Let’s stick to our story about automotive manufacturing. In this sector, AI-driven perception is already improving quality control. Imagine an AI-powered inspection system scanning car doors as they move down the production line. If it detects a misalignment, dent, or scratch, it flags the defect in real time, ensuring that faulty parts don’t make it further into production.
Decision-Making
This one might be a bit obvious, but it’s worth discussing. AI doesn’t just recognize issues, like spotting a dented car door down the assembly line. it can simulate realistic scenarios and make decisions on its own.
Take supply chain disruptions, a constant challenge in automotive production. If a shipment of car doors is delayed, the AI can automatically adjust the production schedule, prioritizing tasks like engine installation or interior assembly instead. Instead of work grinding to a halt, AI keeps operations flowing efficiently.
Physical AI
This is where AI goes beyond automation. We’ve talked about machines that perceive their surroundings and AI systems that can make decisions for efficiency. Does this conversation about autonomous AI sound familiar? Well, physical AI enables machines to take deliberate actions without human intervention through agentic AI. Physical AI enables machines to take action autonomously, learning from past experiences and continuously improving processes.
Take the automotive sector, where AI can predict equipment failures before they happen. If real-time sensor data shows that a robotic arm is likely to overheat in a week, AI can reschedule production, optimize machine workloads, and preemptively dispatch maintenance crews, preventing costly downtime before it even starts.

Implementing AI-Driven Ambient Intelligence
Ambient intelligence has the potential to make factories more productive, but where can manufacturers start? The first step is assessing for AI readiness, followed by AI training and then ensuring continuous learning. Although this is applicable for any manufacturing industry, let’s explore these steps through the lens of our hypothetical automotive factory adopting this technology.
Step 1: AI Readiness
Before manufacturers can fully tap into AI-driven ambient intelligence, they need a strong digital foundation that supports continuous learning and smart decision-making. Here’s what that looks like:
- Infrastructure: AI needs serious computing power, such as high-performance processing, cloud integration, and edge computing, to analyze factory operations in real time. To catch issues like defective auto parts in real time, the AI must process data on the fly. Without enough computing power, it might miss a scratch on a car door or take too long to react, slowing production.
- Data: AI runs on clean, high-quality data to find patterns and predict problems like equipment breakdowns. In that same car factory, sensors track things like paint quality, welding temperatures, and part alignment. If the data is messy or inconsistent, the AI might think a paint flaw is fine, letting defective doors move down the line. With accurate data, the AI can catch those mistakes early, saving time and resources.
- Connectivity: Low-latency, high-bandwidth networks (thanks to industrial 5G, IoT, and machine-to-machine tech) keep everything in sync. Imagine the factory’s conveyor system. If there’s a lag between the AI and the equipment, parts could pile up and cause delays. With real-time communication, the AI can quickly adjust conveyor speeds or reroute parts to keep the production line running.
Step 2: AI Training and Deployment
AI needs to understand real-world factory environments, not just follow pre-programmed instructions. This integration involves three key components:
- Leveraging Sensors: AI relies on sensor data to build a detailed “world model” of the factory. Let me expand a bit on what world foundation models are. They are a type of neural network, simulating real-world environments to predict outcomes based on text, image, or video input. Physical AI systems, like robotic arms in an automotive plant, use these models to accelerate training and testing.
For example, in an automotive factory, a robotic arm installing car engines learns the best speed and angle for installation by analyzing sensor feedback. When a new engine model is introduced, AI simulates the process using its world model, adjusting before real-world errors happen, making transitions smoother and more efficient.
- Virtual Training with Digital Twins: Before deploying AI on the factory floor, it’s a good idea to let it train in a simulated environment, known as digital twins. These virtual versions of the factory enable the AI to test and refine its decisions without disrupting actual production.
For example, when rolling out a new SUV model, the factory can use a digital twin to simulate the assembly process, ensuring all robotic systems work in sync. One critical factor is motion path optimization, where AI analyzes the movement of robotic arms, conveyors, and assembly tools to prevent overlapping work zones or unintended collisions. If the AI detects that two robotic arms risk colliding while installing a new engine configuration, it can adjust their paths in advance, ensuring smooth operations before production even begins.
- Supporting Workers, Not Replacing Them: We’ve said it before and we’ll say it again. AI’s job isn’t to take over. it’s there to help workers do their jobs better. In fact, a recent survey indicated that 90% of workers report that AI has helped them save time on tasks. To illustrate, an AI-powered torque monitoring system can detect when a bolt is under-tightened, alerting workers to verify and correct the issue. This process prevents structural weaknesses while keeping human oversight in the loop.

Step 3: Continuous Learning and Optimization
For AI to really make a difference in manufacturing, it needs to keep learning and adapting as things change. Here’s how it pulls that off:
- Dynamic Adjustments: AI analyzes machine feedback and sensor data to fine-tune production processes in real time. Let’s say temperature sensors in a car factory pick up on a welding station getting too hot. The AI can catch that early, slow things down in that area, and suggest alternate workflows to keep production moving without risking equipment damage.
- Refined Decision-Making: By looking at past performance data, AI spots trends, manage bottlenecks, and adjust for changes in the environment. For instance, over several months, the AI tracks how long it takes to install sunroofs during peak production. It notices things slow down at certain times and realizes shifting that task earlier in the schedule could speed up production. Based on this insight, AI recommends a new workflow that saves time without sacrificing quality.
- Human-AI Collaboration: AI isn’t working in a vacuum—it learns from people, too. Human operators bring context that machines alone can’t pick up. For instance, if AI recommends rerouting a task, a worker might spot a potential bottleneck that AI overlooked (yes, it can happen). By integrating human feedback, AI adjusts its strategy, ensuring smoother operations and smarter decision-making.
Where IoT Fits In
Sensors and edge computing team up to provide AI the real-time data it needs to make smart decisions. These sensor-rich environments include:
- Temperature sensors to catch overheating equipment
- LiDAR sensors that create 3D maps of the factory floor
- Vision cameras to find product defects
- Ultrasonic detectors that measure distances and detect objects
- Motion sensors that track equipment and worker movements
In an automotive factory, IoT sensors feed AI the real-time data it needs to optimize operations. Vision cameras inspect car doors for paint defects, while motion sensors track robotic arms. If AI detects an arm slowing down, it flags the issue instantly, preventing disruptions.
Edge computing processes sensor data on-site, enabling real-time adjustments. For instance, if AI detects an uneven windshield seal, it immediately tweaks the adhesive application, ensuring precision without delays. As AI continuously analyzes sensor data, it learns, adapts, and optimizes processes, driving factories to become smarter and more efficient over time.
Business Impact: What’s Achievable Today?
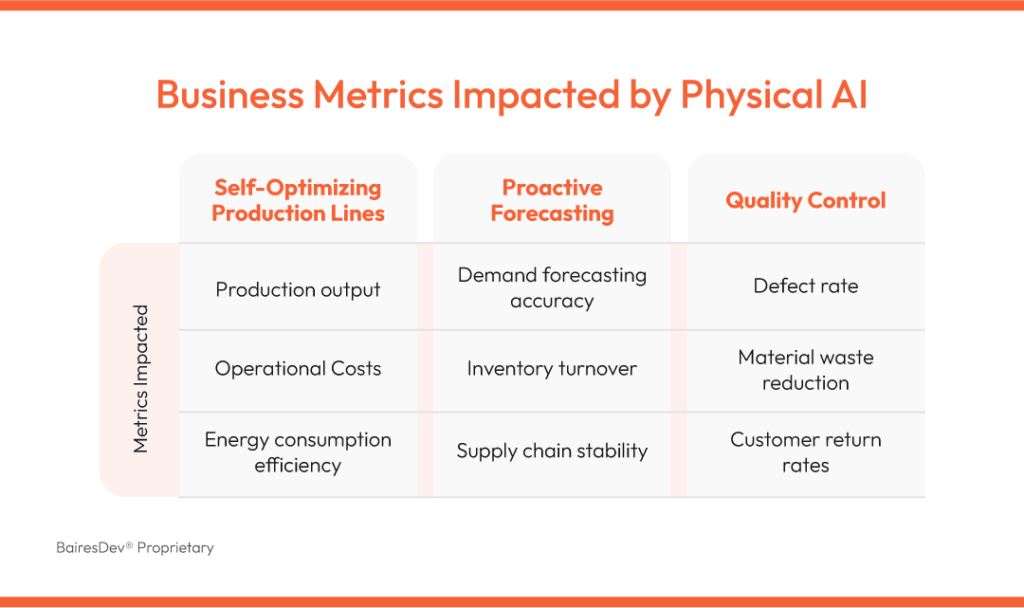
What does all this mean in business terms? Simply put, physical AI goes beyond automating basic tasks, it directly improves profitability. Optimizing production efficiency, reducing errors, and cutting costs, AI significantly impacts a company’s bottom line. Here are the top three areas where businesses see the biggest benefits:
- Self-Optimizing Production Lines: AI-driven systems analyze operations in real time, adjusting workflows to increase output and optimize energy use. This results in higher production rates and lower costs, all with minimal human intervention.
- Key Metrics Impacted: Production output, operational costs, energy consumption efficiency
- Proactive Forecasting: AI can anticipate product demand, supply chain disruptions, and quality issues before they occur after analyzing economic changes, potential supply shortages, and environmental data.
- Key Metrics Impacted: Demand forecasting accuracy, inventory turnover, supply chain stability
- Autonomous Quality Control: AI monitors products continuously, identifying and preventing defects before they reach final production. This reduces rework, minimizes waste, and improves customer satisfaction.
- Key Metrics Impacted: Defect rate, material waste reduction, customer return rates
The impact is tangible. Real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance can increase uptime by up to 15%, cutting down on costly breakdowns. AI-powered defect detection improves product quality by 35%, reducing waste and production errors. And according to PwC, AI-driven automation can boost manufacturing output by as much as 20%.
The Road to Smarter Manufacturing
Ambient intelligence is reshaping manufacturing. Creating digital environments that can sense their surroundings and take action without human input has the power to make production lines more efficient, reduce errors, and increase overall productivity.
For business leaders in this sector, now is the time to explore AI integration. Implementing ambient intelligence and physical AI can lead to substantial savings in both time and costs while improving supply chain operations. If you’re ready to integrate these AI solutions, our team can help your business drive efficiency, cut costs, and future-proof operations. Let us help you take the next step toward smarter manufacturing.